L’pelargonic acid it is a naturally occurring organic compound, which can be used as a natural herbicide in organic farming. This acid is present in many plants, but is mainly extracted from geranium (Pelargonium graveolens)from which its name derives. It can be an effective option in organic farming, especially when used in conjunction with other weed control methods.
In this article we will see the advantages and disadvantages of this organic product and understand how to use it in the garden.
What is pelargonic acid and how does it work as a herbicide?
Pelargonic acid acts as a selective contact herbicide, ie it acts only on the parts of the plants with which it comes into contact, without penetrating the vascular system of the plant itself. When applied to weed leaves, this biological herbicide penetrates plant cells, causing them to dehydrate and die. In particular, pelargonic acid acts on the cuticle of the plant, i.e. the outer part of the leaves which protects it from water evaporation, damaging it and causing water to leak from the plant cells.
How to use pelargonic acid in organic farming?

Pelargonic acid can be used in organic agriculture to control weeds in various types of crops, such as vegetables, orchards, vineyards and ornamental plants. There are several products on the market based pelargonic acid on the market, in the form of a liquid or granular solution, which can be applied by spraying or spraying. For best results, it is important to apply this organic product on actively growing weeds, when the plants are still young and have not yet reached full maturity. Also, pelargonic acid is most effective when applied to weeds that are not too tall, as the solution may not reach the lower parts of taller plants.
What are the pros and cons of using pelargonic acid in organic farming?
The use of pelargonic acid as a herbicide in organic farming has several advantages over the use of chemical herbicides. Firstly, it is a natural and biodegradable product, which leaves no harmful residues in the environment and does not harm human health. Furthermore, it is a selective herbicide, which acts only on the parts of the plants it comes into contact with, without damaging the surrounding cultivated plants.
However, using pelargonic acid also has some disadvantages. First, it is a relatively expensive commodity, which could pose an economic challenge for farmers. Also, its effectiveness may vary depending on environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity. These can affect the product’s ability to penetrate weed leaves. Finally, it is not effective against all weed species, and in some cases it may be necessary to use other integrated control methods, such as crop rotationthe ground cover or the use of manual techniques.
How is it chemically composed?
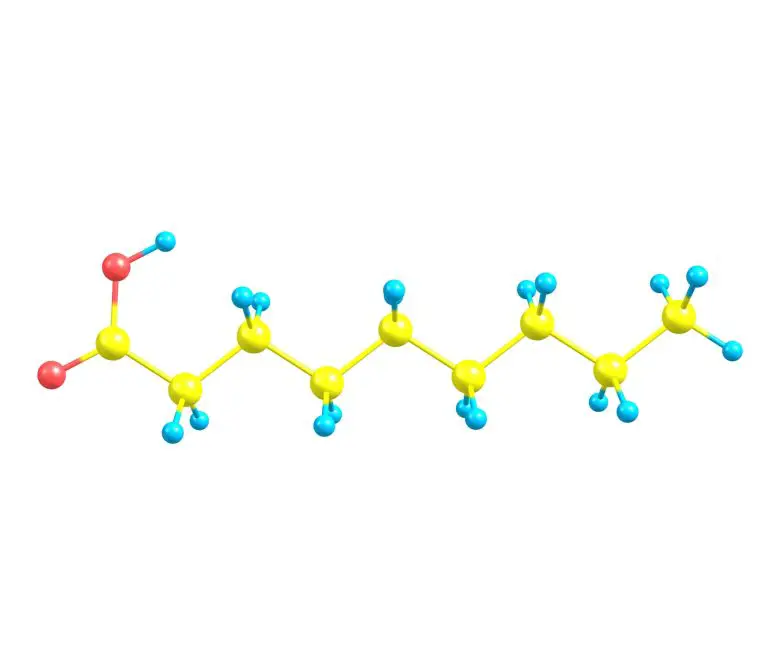
Pelargonic acid, also known as nonanoic acid, is a nine-carbon carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is C9H18O2 and its molecular structure is characterized by a carboxyl group (-COOH) at the end of a carbon chain of eight carbon atoms, with a methyl group (-CH3) at the other end of the chain.
This acid can be produced both synthetically and naturally, through the microbial fermentation of renewable sources such as vegetable oils and animal fats. In nature, pelargonic acid is present in small quantities in some plants, such as geranium (hence the name “pelargonic”). It is also produced by the cells of some bacterial and fungal species. For use in organic farming, it is usually produced synthetically, but the final product is identical to that obtained naturally. Pelargonic acid is an authorized product in organic farming. Also, it is regulated by the European Union and is considered safe for the environment and human health when used correctly.







Start a new Thread