The manure and the organic fertilizer for excellence. It is a substance that derives from both solid and liquid manure of some animals and from the litter. It has always been used in agriculture for its nutritional properties for the benefit of plants.
In ancient times the manure produced by animals they were part of the normal production cycle of the farm, thanks to their use as fertilizer and soil improver.
Today, with the specialization of agricultural activities, it is difficult to find companies that integrate animal breeding and cultivation of vegetables.
It is also increasingly difficult to find a good product from organically-run farms. Not all manure, in fact, can be used in organic farming, but only that deriving from sustainably managed animal farms.
In this article we see an overview on the use of manure to improve the quality of our organic crops, investigating the different practical implications point by point.
Manure as an organic fertilizer
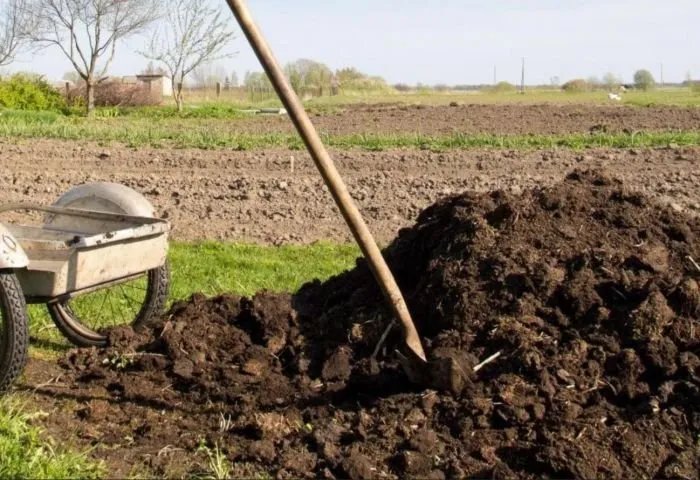

In organic farming, manure can be considered the best source of organic matter. It is indispensable for make the soil fertile and ensure healthy and lush growth of plants.
Soil fertility has several aspects. First of all the microbiological one, that is to say the presence in the soil of microorganisms useful for the elaboration of the nutrients necessary for the crops. Animal droppings contain large quantities of it and contribute to the formation ofhumusterm with which we indicate the organic substance present in the soil.
Manure is already nutritional humus in itself, that is the set of substances that can be readily decomposed and mineralized by bio-reducing microorganisms. Furthermore, over time it becomes stable humus, which is a lasting reserve of nutritional elements that the roots of plants can draw on. Therefore, it is a real one natural fertilizer.
How is manure made?
Manure does not consist exclusively of animal manure. In fact, the origin of the litter and the livestock production methods influence the exact composition. The first can consist of cereal straw, corn stalks, shavings, hay, etc. As regards livestock production, on the other hand, the variables can be: composition of the litter, quantity and timing of distribution of the plant material, management of the stable, etc.
What nutrients does it contain?
The addition of manure with periodic fertilizations improves the chemical composition of the soil, transforming itself into a sort of “bank” in which the basic elements for the growth of plants in the different phases of their biological cycle are contained, namely: nitrogen, phosphorus And potassium.
In addition to these basic elements, manure contains:
- mesoelements, such as: calcium, magnesium and sulfur
- microelements, such as: iron, zinc, copper, boron, etc.
They are all important components for the harmonious development of plants and for growing quality fruit and vegetables.
Let’s not forget that healthy and luxuriant plants hardly get sick. Thus, by improving the agricultural soil, this fertilization becomes a natural defense against soil parasites (nematodes) and diseases.
Manure as a soil improver
Adding manure to the soil changes it and also improves it physical characteristicshence its structure.
An abundantly fertilized soil has these advantages:
- it is easier to work with;
- it is softer in the superficial layers, which facilitates sowing and transplanting;
- it has a better ability to absorb excess water, thus avoiding dangerous water stagnation;
- allows a greater availability of water for crops in periods of drought;
- it can also be used to correct particularly difficult soils, such as those that are too clayey and compact.
Is the manure organic?
Not all manure is organic, as not all animal farms are managed equally.
In organic farming, only that coming from organically conducted livestock farms can be used.
The reference legislation is the Regulation (EC) n. 834/2007 (integrated with the relative national provisions).
These texts clarify the criteria for considering organic livestock farming. Furthermore, the use of animal manure (fresh or dried) from industrial farms is prohibited in horticulture.
Industrial farms
Industrial farms do not allow amending healthy manure to the soil. This leads as a consequence that we may find ourselves in the paradox of worsening the conditions of our soil, rather than improving them.
Modern stables produce mostly slurry, which does not contain plant material and which does not give rise to the formation of humus.
Which manure to choose
The various types

Of course, animal manure is not all the same, as there are different animal species that produce manure.
In agriculture, the most used manures for organic fertilization are:
Each of these types has a different composition, made of water and dry matter (whose organic substance is mainly composed of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium).
In the following table we observe the average values of the composition of 100 quintals of manure. We indicate in “%” the quantity of water and dry matter present on average in the different types. In “kg”, on the other hand, the nutrients supplied by organic substance, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium are expressed.
The reference is to fresh manure.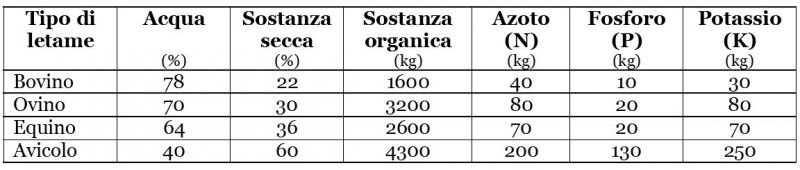
Poultry
As can be seen from the table, the poultry manureor droppings, is the richest in nutrients. The problem is that the one from organic farms is very difficult to find. The idea would be to have your own chicken coop, from which to take it and keep it.
Companies that produce organic eggs, with sustainable farms, usually have land on which they produce vegetables using their own manure, so they do not sell it to third parties.
The droppings coming from hens reared inside the industrial sheds, whether they are on the ground or in cages, are to be absolutely avoided.
Bovine
Cow manure is probably easier to find, but it must be said that it is the poorest in organic matter and elements.
Sheep
Sheep manure is excellent in terms of composition. In the areas where sheep and goats are raised, it is not difficult to find organic livestock farms, which will gladly sell you a good product.
Equine
Horse manure is probably the most practical solution. There are many riding schools in our countryside, where animals are raised correctly. Usually, those who do horse riding do not practice intensive horticulture, so it is easier to find excellent horse manure.
The right ripening of the manure
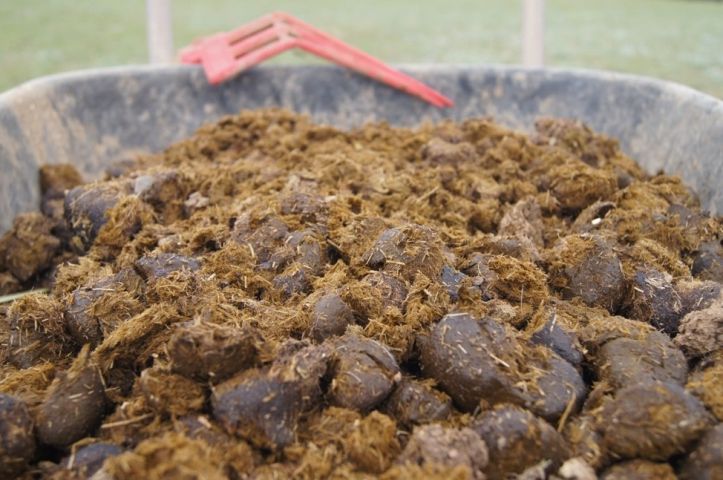

When we talk about manure we must take into account its different degree of ripeness.
In this sense we distinguish three types:
- Fresh;
- Mature;
- Composted.
Fresh
Fresh manure is the one with less than three months of maturation. It is strongly not recommended to spread it on the ground.
In fact, this typology, in addition to still containing a lot of inert plant material, can contain seeds of weeds, fungi, parasites and unwanted bacteria. Amended immediately to the ground, it could accidentally make us sow crops that we are not interested in (grasses). In addition to the fact that it is very risky for the crop with which it comes into contact, which can be “burned” by the high temperature that the fresh material develops and by the ammonia nitrogen component present in it.
Mature
The manure to be used for fertilizing the organic garden is the most mature possible. With this term we mean the one with 9-10 months of maturation.
The maturation process takes place with fermentation. High temperatures develop inside the heap, which after a certain period of time, thanks to the action of microorganisms, consume harmful seeds, fungi and bacteria.
When the manure is mature, it looks a lot like good soil, it is dark in color and the plant material inside it is totally degraded. In these conditions the nutritional elements are stabilized and readily available for the roots of the plants, which does not happen when the product is fresh.
It is possible to amend the soil even a few days before sowing and transplanting, without running any risk.
Composted
With the term composted manure means the one with more than 12 months of maturation. The composting process must be done correctly.
How to compost manure correctly
Having established the fact that mature manure is what must be used as organic fertilizer, let’s understand how it is composed correctly.
Let’s assume that you have been given a fresh product as a gift, which is quite probable, as making it mature has a certain cost for the livestock farm. Manure typically keeps in heaps. For mature properly the heap must be covered, i.e. not exposed to the action of atmospheric agents (water and sun).
One solution is therefore to have the shelter of a canopy, where water and sun do not reach the mound. If you don’t have a canopy you can use a waterproof pvc sheet (adaptable to different uses).
To speed up composting, another trick is to periodically turn the pile over. We can observe that the external part is the one that dries first, as it is in the center of the heap that fermentation processes take place and heat develops. Turning it over periodically will guarantee us, at the end of the process, a mature manure in a homogeneous way and in a shorter time.
Turning it over also gives us a visual indication of the degree of ripeness. When we observe that no more “smoke” rises from the center of the heap and no “heat” is felt, our organic fertilizer is ready to be amended for the garden soil.
When to use manure
Manure the garden
We cannot establish an exact time for the distribution of manure on the ground. If it is very mature we can amend it on the cultivation soil even 15 days before the start of the cycle, that is the moment of sowing or transplanting.
Usually, fertilization takes place between late winter and early spring, at the start of a long cultivation cycle.
Others fertilize with manure in the fall, that is, at the end of the long summer cycles. This solution may be valid, but exposes the organic substance to the degradation of the entire winter season, which in fact could be consumed. By fertilizing in autumn we will find ourselves in spring with a less “powerful” product.
Manure the orchard
Different speech can be made for fertilizing with manure organic orchard.
First of all, the mature manure is added at the moment of planting, placing it on the bottom of the hole where we will go to plant the new tree. In doing so, the roots of the plant they will have sufficient nutrients available for the delicate initial phase of rooting.
Then there is the annual fertilization, which is done in autumn or at the end of winter. In this case, mature manure must be amended for the orchard soil.
Recall that part of the root system of trees is superficial, so hoeing to amend the manure must be light.
All fruit crops benefit from periodic manuring, including those ofolive tree and of lives.
What are the crops that require manure
In the garden there are crops that require more manure, others less.
More demanding crops
Among the most “greedy” crops we certainly have:
- Solanaceae (tomato, aubergine, sweet pepper, potato, tamarillo, chili pepper);
- Cucurbits (zuchini, cucumber, pumpkin, melon, loofah, watermelon);
- Cruciferous (cauliflower, savoy cabbage, black cabbage, cabbage).
Less demanding crops
Less demanding crops in terms of manure are the Leguminous plants (green beans, Fava beans, beans, chickpeas, lentils, peas, lupins, peanuts).
Other crops, such as Liliaceae (garlic, onion, leek, shallot), do not like strong organic fertilization before the start of the cycle.
Manure according to crop rotations
Given the different needs of the various crops, it is therefore necessary to think in terms of crop rotations.
Suppose we have a small piece of land lying dormant for a long time, where in the first year we want to grow tomatoes and zucchini.
In this case, a good initial manure is advisable, so as to be able to give these very demanding plants the maximum supply of nutrients and organic matter.
At the end of the first cycle we can decide to sow legumes, for example broad beans, without doing any type of fertilization.
After harvesting the beans, in the spring of the second year, we will be able to exploit this piece of land to grow onions.
In practice, the manure of the soil does not necessarily have to be annual, but must precede the cultivation of crops greedy for organic matter.
On average, a manure every two years should satisfy this need.
The right amount of manure in the soil
Another question that always arises is: how much manure to put in the ground?
In agricultural texts you will find a distribution per hectare measured in quintals. Here we try to think for a small family garden, speaking of kg per square meter.
If you have manure, then poultry manure, a small amount is enough, about 1 kg per square meter cultivated.
For mature bovine manure we can quadruple this quantity, making about 4 kg of manure per square meter.
With sheep or horse manure we adjust to the center of this fork and we will fine the ground about 2-3 kg of manure per square meter.
How to distribute the manure
Another problem is that of the distribution of manure on the ground, which must be as uniform as possible.
If the fertilizer spreader brought by the tractor is used on large plots, in a small vegetable garden it is done by hand.
The tools needed are:
- shovel or pitchfork to impale
- wheelbarrow to carry
- fork with bent teeth or rake to distribute evenly
Fertilizing with manure is a very heavy job, which would be better to do at least in two, in order to divide the tasks.
One person to fill the wheelbarrow, another to spread on the ground.
When the manure is evenly distributed, it will need to be amended, that is, processed.
If we work completely by hand, we can carry out a dig.
If we have a motor hoe or a walking tractor at our disposal, we try not to let the organic substance go too deep. The buried manure should not descend to the soil more than 15-20 cm.
The pelleted manure
As we have emphasized several times, it is not always easy to find animal manure, even mature. For the organic fertilization of the gardentherefore, the commercial alternative is represented by the pelleted manure (or synthetic manure).
It is dry and compacted manure, which has been almost completely removed from the water, which is sold in bags.
There are different types and compositions that you can safely find in specialized stores.
They can be considered excellent organic fertilizers. They are applied in smaller quantities, but have a fairly high cost, especially for medium-large extensions.
Compared to manure, they do not have the amending function, that is, they are not able to significantly modify the structure of the soil.







Start a new Thread