We put the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra through our rigorous SBMARK Camera test suite to measure its performance in photo, video, and zoom quality from an end-user perspective. This article breaks down how the device fared in a variety of tests and several common use cases and is intended to highlight the most important results of our testing with an extract of the captured data.
Overview
Key camera specifications:
- Primary: 200MP 1/1.3″ sensor, 0.6 μm pixels, f/2.2-aperture lens, PDAF, AF, OIS
- Ultra-wide: 12MP 1/2.55″ sensor, 1.4 μm pixels, f/2.2-aperture lens, PDAF, AF, OIS
- Tele 1: 10MP 1/3.52″ sensor, 1.12 μm pixels, f/2.4-aperture lens, PDAF, OIS, 3x optical zoom
- Tele 2: 10MP 1/3.52″ sensor, 1.12 μm pixels, f/4.9-aperture lens, PDAF, OIS, 10x optical zoom
Pros
- Very good detail
- Fairly wide dynamic range in all conditions
- Good detail across most zoom settings
- Very effective video stabilization
- Accurate autofocus in both photo and video
Cons
- Low contrast in backlit scenes
- Noise in low light and indoors
- Occasional local loss of detail on faces
- Fusion artifacts in all conditions
- Slight white balance casts
- Occasional underexposure of faces in low-light video
With a SBMARK Camera score of 140, the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra achieved a very good result in our camera tests. It offered good performance across pretty much all test attributes, without major drawbacks in any area, making it a great smartphone imaging allrounder. Still images featured excellent detail in bright light and a fairly wide dynamic range across all light levels. Please note that still-image testing was undertaken at the default 12MP resolution. The camera also allows for capture at higher image resolutions.
Tele zoom at very long range was a strength, thanks to Samsung’s dual-tele approach with a dedicated 10x camera. However, despite the sophisticated tele hardware, overall zoom results were slightly below competitors such as the Huawei Mate 50 Pro or Honor Magic 4 Ultimate, which provide more consistent tele zoom quality with only one higher-resolution tele camera module.
Effective stabilization and a fast and accurate autofocus meant that the Galaxy S23 Ultra also did well for video. White balance in low light left some room for improvement, though. Compared to the predecessor S22 Ultra, the Samsung engineers managed to achieve improvements in several areas, including video stabilization, slightly better zoom, noticeably better video exposure, and improved autofocus speed in bright light. Please note that all comparisons with the S22 Ultra in this review were made with the Snapdragon version of that device. The S23 Ultra only comes as a Snapdragon variant. Unlike for previous generations, there is no Exynos-powered version.
Friends & Family
Friends & Family is a new use case score, introduced with the latest version 5 of the SBMARK Camera test protocol. It has been designed to represent the test device’s ability to capture technically good photos and videos in the most common consumer use cases (family, friends, pets). It is computed from data recorded during Photo, Zoom and Video tests that include people and moving subjects, a total of 60+ scenes both in the lab and real-life scenes with models.
The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra is very capable of taking good quality portrait photos and videos in most lighting conditions. The device’s autofocus was very performant, managing to capture the decisive moment both in indoor and outdoor conditions. In low-light situations, however, our engineers observed a slight delay between the moment the shutter was triggered and the actual capture. Exposure in photo was generally well managed, except when it came to challenging backlit situations, where low contrast gave faces an unnatural appearance. While the S23 Ultra managed to keep the scene’s natural color atmosphere, skin tones were sometimes rendered inaccurate. When taking videos, face tracking was very efficient, keeping moving subjects’ faces in focus.
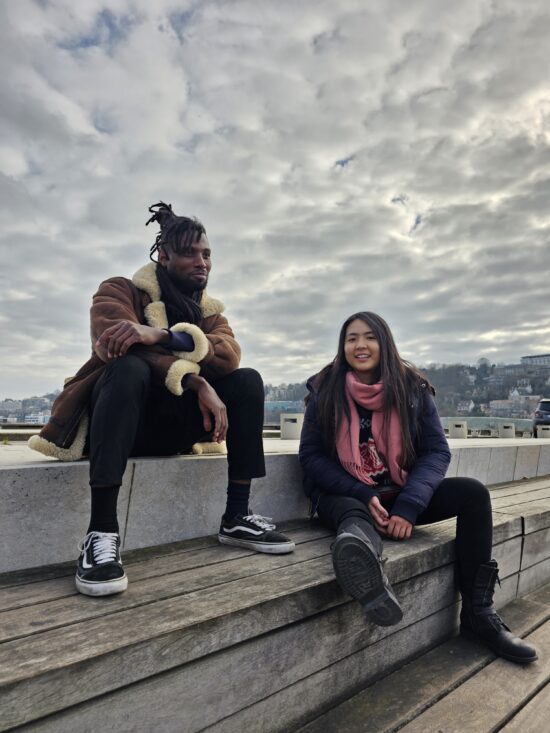

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – High level of detail, nice color rendering, and wide dynamic range (but slight halo effect around subjects)
Lowlight
In low light, the S23 Ultra produced good exposure with a quite wide dynamic range, capturing decent detail in both the highlight and shadow regions of the frame. In terms of color, the engineers opted for maintaining some of the atmosphere that is produced by dim warm light sources, delivering overall nice color in low light. Many competitors tend to take a more neutral approach to white balance in low light, but what you prefer is pretty much down to personal taste.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Warm and pleasant colors, good exposure, fairly good detail but noise in the shadow areas
Test summary
About SBMARK Camera tests: SBMARK’s Camera evaluations take place in laboratories and in real-world situations using a wide variety of subjects. The scores rely on objective tests for which the results are calculated directly by measurement software on our laboratory setups, and on perceptual tests in which a sophisticated set of metrics allow a panel of image experts to compare aspects of image quality that require human judgment. Testing a smartphone involves a team of engineers and technicians for about a week. Photo, Zoom, and Video quality are scored separately and then combined into an Overall score for comparison among the cameras in different devices. For more information about the SBMARK Camera protocol, click here. More details on smartphone camera scores are available here. The following section gathers key elements of SBMARK’s exhaustive tests and analyses. Full performance evaluations are available upon request. Please contact us on how to receive a full report.
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra Camera Scores vs Ultra-Premium
This graph compares SBMARK photo, zoom and video scores between the tested device and references. Average and maximum scores of the price segment are also indicated. Average and maximum scores for each price segment are computed based on the SBMARK database of devices tested.
Photo
139
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
About SBMARK Camera Photo tests
For scoring and analysis, SBMARK engineers capture and evaluate more than 2,600 test images both in controlled lab environments and in outdoor, indoor and low-light natural scenes, using the camera’s default settings. The photo protocol is designed to take into account the main use cases and is based on typical shooting scenarios, such as portraits, family, and landscape photography. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting images Cons a reference of natural scenes, and by running objective measurements on images of charts captured in the lab under different lighting conditions from 1 to 1,000+ lux and color temperatures from 2,300K to 6,500K.
In our tests, the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra performed well for still imaging, capturing impressively high levels of detail in landscape shots. The wide dynamic range is a slight improvement over the predecessor S22 Ultra, and ensured good highlight and shadow detail, even when capturing difficult high-contrast scenes. On the downside, in backlit portrait scenes, a lack of contrast on faces resulted in an unnatural look, and in dim light conditions, image noise could become quite intrusive.
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra Photo scores vs Ultra-Premium
The photo tests analyze image quality attributes such as exposure, color, texture, and noise in various light conditions. Autofocus performances and the presence of artifacts on all images captured in controlled lab conditions and in real-life images are also evaluated. All these attributes have a significant impact on the final quality of the images captured with the tested device and can help to understand the camera’s main strengths and weaknesses.
Close-Up
Close-up is the third new use case score introduced with SBMARK Camera version 5. It evaluates the camera’s ability to capture detail at subject distances below 10cm and magnifications as close as possible to 1:1.
The Galaxy S23 Ultra did a good job of capturing detail in macro mode. In addition, macro images featured pleasantly bright colors. On the downside, noise was quite noticeable when viewing the images up close, and a visible regression compared to the S22 Ultra was noticeable.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Macro

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Noise

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Macro

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Well-controlled noise

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Macro

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Well-controlled noise
Exposure
105
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
Exposure is one of the key attributes for technically good pictures. The main attribute evaluated is the brightness of the main subject through various use cases such as landscape, portrait, or still life. Other factors evaluated are the contrast and the dynamic range, eg. the ability to render visible details in both bright and dark areas of the image. Repeatability is also important because it demonstrates the camera’s ability to provide the same rendering when shooting several images of the same scene.
In terms of exposure, the Galaxy S23 Ultra is a slight improvement over its predecessor the S22 Ultra. In our tests, dynamic range was slightly wider on the new model, and in these samples, you can see the S23 Ultra preserved a touch more detail in the clipped background of the image.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Dynamic range

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Highlight clipping

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Dynamic range

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Slightly stronger clipping
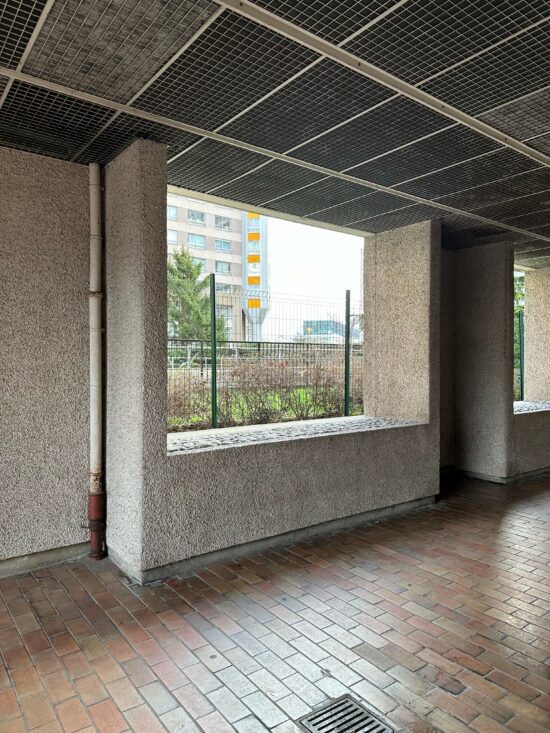

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Dynamic range

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Strong highlight clipping
The very slight improvement compared to S22 Ultra was also visible in our contrast entropy tests in the lab. For this test, we vary the brightness of a backlit panel of grayscale blocks to increase or decrease the brightness difference to a Dead Leaves chart in the same test setup. As you can see, the S23 Ultra delivered slightly better entropy than the comparison devices across pretty much all light conditions.
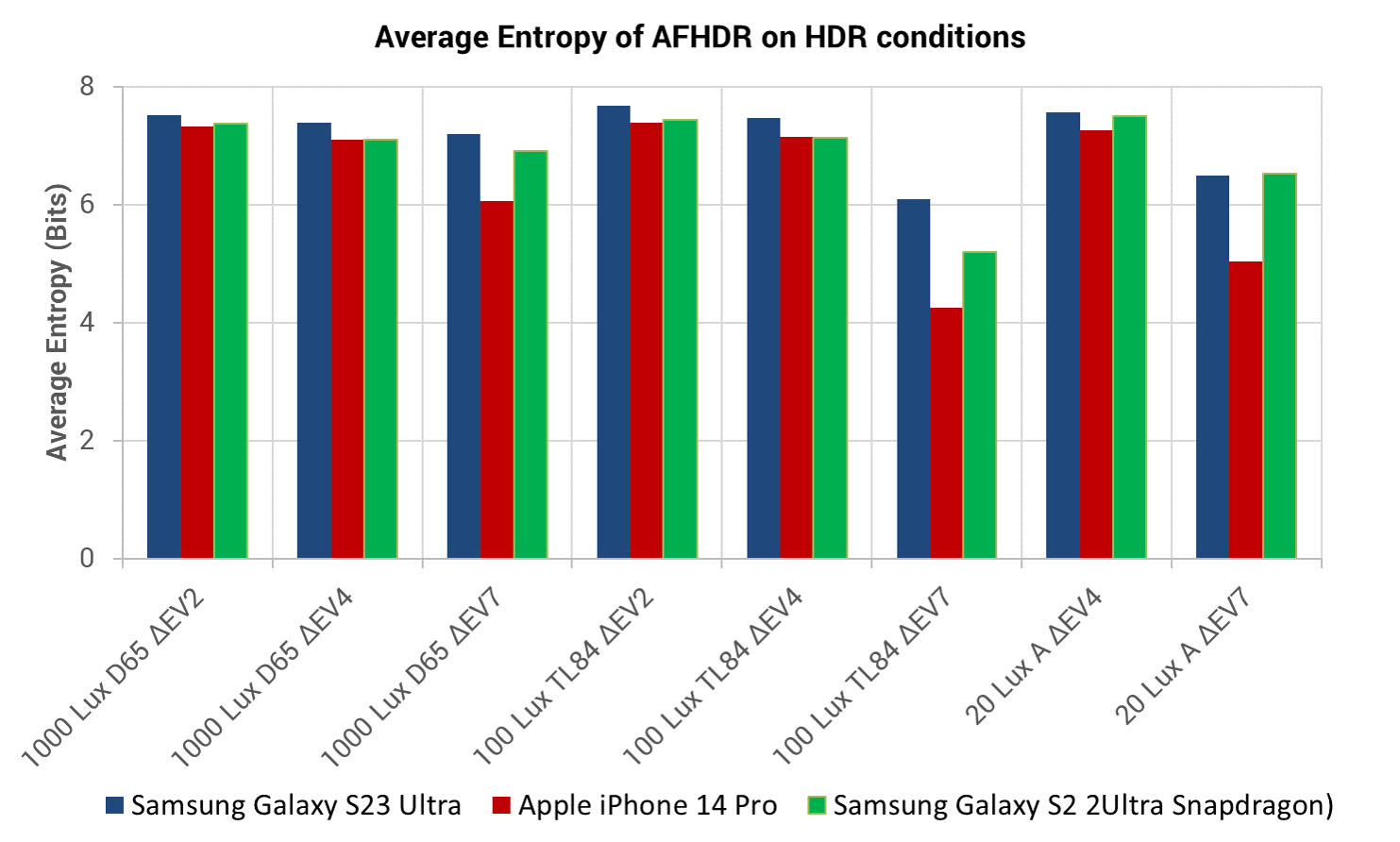
Contrast entropy: The S23 Ultra offered slightly better highlight recovery capability than the S22 Ultra in most conditions. It was noticeably better than the iPhone 14 Pro in high-contrast scenes.
Exposure instabilities were an issue though, with noticeable exposure differences between consecutive shots of the same scene. In comparison, the iPhone 14 Pro was much more consistent. Tone compression on faces was another weakness in terms of exposure. In this sample contrast is low on the faces, resulting in an unnatural effect.
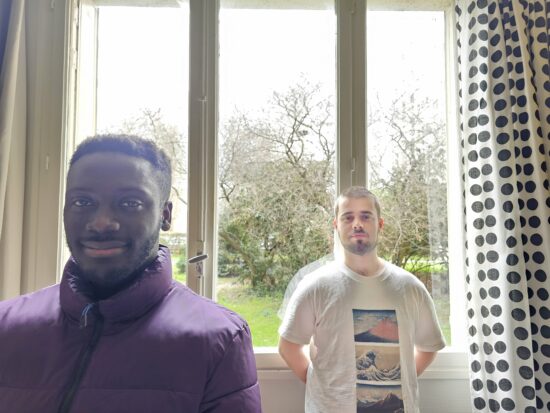

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Low contrast on faces

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Slightly low contrast on faces

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Nice contrast on faces
Color
113
Google Pixel 7 Pro
Google Pixel 7 Pro
Color is one of the key attributes for technically good pictures. The image quality attributes analyzed are skin-tone rendering, white balance, color shading, and repeatability. For color and skin tone rendering, we penalize unnatural colors but we respect a manufacturer’s choice of color signature.
The S23 Ultra was capable of maintaining vibrant color and a scene’s natural color atmosphere down to low-light conditions. In this scene, the ambient lighting´s slightly warm cast has been nicely preserved.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Nicely warm white balance

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Slight pink rendering

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Yellow/Green cast
On the downside, skin tones were sometimes rendered unnaturally desaturated and with noticeable color quantization.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Skin tones

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Desaturated skin tones, color quantization

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Skin tones

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Desaturated skin tones

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Skin tones

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Nicely saturated skin tones
Autofocus
112
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
Autofocus tests concentrate on focus accuracy, focus repeatability, shooting time delay, and depth of field. Shooting delay is the difference between the time the user presses the capture button and the time the image is actually taken. It includes focusing speed and the capability of the device to capture images at the right time, what is called ‘zero shutter lag’ capability. Even if a shallow depth of field can be pleasant for a single subject portrait or close-up shot, it can also be a problem in some specific conditions such as group portraits; Both situations are tested. Focus accuracy is also evaluated in all the real-life images taken, from infinity to close-up objects and in low light to outdoor conditions.
The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra was overall a very good performer for autofocus, with fast capture in bright light and under indoor illumination, even in high-contrast conditions. This is a significant improvement over the S22 Ultra, which took longer to capture images in outdoor conditions.
Autofocus irregularity and speed: 1000Lux Δ7EV Daylight Handheld
This graph illustrates focus accuracy and speed and also zero shutter lag capability by showing the edge acutance versus the shooting time measured on the AFHDR setup on a series of pictures. All pictures were taken at 1000Lux with Daylight illuminant, 500ms after the defocus. On this scenario, the backlit panels in the scene are set up to simulate a fairly high dynamic range: the luminance ratio between the brightest point and a 18% reflective gray patch is 7, which we denote by a Exposure Value difference of 7. The edge acutance is measured on the four edges of the Dead Leaves chart, and the shooting time is measured on the LED Universal Timer.
However, there was a noticeable drop in performance in low light, with the Samsung taking a lot longer to capture the image than the iPhone.
Autofocus irregularity and speed: 20Lux Δ7EV Tungsten Handheld
This graph illustrates focus accuracy and speed and also zero shutter lag capability by showing the edge acutance versus the shooting time measured on the AFHDR setup on a series of pictures. All pictures were taken at 20Lux with Tungsten illuminant, 500ms after the defocus. On this scenario, the backlit panels in the scene are set up to simulate a fairly high dynamic range: the luminance ratio between the brightest point and a 18% reflective gray patch is 7, which we denote by a Exposure Value difference of 7. The edge acutance is measured on the four edges of the Dead Leaves chart, and the shooting time is measured on the LED Universal Timer.
The delayed capture in low light is illustrated in this sample. In this scene, the trigger is actuated as the person passes by the wall. The iPhone did an excellent job and captured the image immediately. Both Samsung devices were noticeably slower and captured the image only after the subject had moved closer toward the camera.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Delayed capture, later than intended by photographer

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Delayed capture, later than intended by photographer

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Immediate capture, when intended by photographer, but underexposure on face
Texture
113
Oppo Find X5
Oppo Find X5
Texture tests analyze the level of details and the texture of subjects in the images taken in the lab as well as in real-life scenarios. For natural shots, particular attention is paid to the level of details in the bright and dark areas of the image. Objective measurements are performed on chart images taken in various lighting conditions from 1 to 1000 lux and different kinds of dynamic range conditions. The charts used are the proprietary SBMARK chart (DMC) and the Dead Leaves chart.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score vs lux levels for tripod and handheld conditions
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with the level of lux, for two holding conditions. DMC detail preservation score is derived from an AI-based metric trained to evaluate texture and details rendering on a selection of crops of our SBMARK chart.
The S23 Ultra did a good job of capturing image detail across all light conditions. In this shot, captured under indoor lighting, the improvement over the S22 Ultra is quite noticeable.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Texture

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Good detail

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Texture

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Slight loss of detail

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Texture

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Good detail
However, our testers observed a local loss of sharpness in some scenes. In this image, the level of sharpness is not consistent across the face in the foreground.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Texture

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Slight local loss of sharpness on face
Noise
90
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
Noise tests analyze various attributes of noise such as intensity, chromaticity, grain, structure on real-life images a-cs well as images of charts taken in the lab. For natural images, particular attention is paid to the noise on faces, landscapes, but also on dark areas and high dynamic range conditions. Noise on moving objects is also evaluated on natural images. Objective measurements are performed on images of charts taken in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux and different kinds of dynamic range conditions. The chart used is the Dead Leaves chart and the standardized measurement such as Visual Noise derived from ISO 15739.
Overall, the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra did a good job at controlling image noise levels and balancing it with texture. However, in some scenes, such as the one below, our testers observed unexpectedly high luminance noise.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Noise

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Strong noise

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Noise

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Slight noise

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Noise

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Slight noise
Artifacts
71
Google Pixel 6
Google Pixel 6
The artifacts evaluation looks at lens shading, chromatic aberrations, geometrical distortion, edges ringing, halos, ghosting, quantization, unexpected color hue shifts, among others type of possible unnatural effects on photos. The more severe and the more frequent the artifact, the higher the point deduction on the score. The main artifacts observed and corresponding point loss are listed below.
Main photo artifacts penalties
We found a variety of image artifacts in our S23 Ultra sample shots, the most prevalent being fusion artifacts, like the ones visible in this scene. This said, the mixed low-level lighting made for difficult conditions to shoot in.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Artifacts

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Fusion artifacts
Ringing artifacts were also visible on high-contrast edges in some scenes.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Artifacts

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Ringing
Bokeh
70
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
Bokeh is tested in one dedicated mode, usually portrait or aperture mode, and analyzed by visually inspecting all the images captured in the lab and in natural conditions. The goal is to reproduce portrait photography comparable to one taken with a DLSR and a wide aperture. The main image quality attributes paid attention to are depth estimation, artifacts, blur gradient, and the shape of the bokeh blur spotlights. Portrait image quality attributes (exposure, color, texture) are also taken into account.
The 23 Ultra captures bokeh shots at a measured 35mm-equivalent focal length of 67mm, which is a very suitable focal length for portraits and quite close to the S22 Ultra. In fact, the look of the S23 Ultra bokeh shots was overall quite similar to those of its predecessor, with natural rendering and good subject isolation from the background. However, some slight segmentation artifacts in complex scenes meant that it wasn’t quite on the same level as the best in class.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Bokeh mode under 50 lux

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Segmentation error
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Bokeh mode under 50 lux

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Segmentation error

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Bokeh mode under 50 lux

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Slight segmentation errors, lower blur intensity
Preview
73
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Preview tests analyze the image quality of the camera app’s preview of the image, with particular attention paid to the difference between the capture and the preview, especially regarding dynamic range and the application of the bokeh effect. Also evaluated is the smoothness of the exposure, color and focus adaptation when zooming from the minimal to the maximal zoom factor available. The preview frame rate is measured using the LED Universal Timer.
The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra achieved a fairly good score in the preview category, but could not quite match the iPhone 14 Pro, which managed much more similar exposure between the preview image and final capture.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Capture

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Preview – Strong dynamic range difference between capture and preview, highlight clipping

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Capture

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Preview – Slight exposure difference between capture and preview
Zoom
141
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
About SBMARK Camera Zoom tests
SBMARK engineers capture and evaluate over 400 test images in controlled lab environments and in outdoor, indoor, and low-light natural scenes, using the camera’s default settings and pinch zoom at various zoom factors from ultra wide to very long-range zoom. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting the images Cons a reference of natural scenes, and by running objective measurements of chart mages captured in the lab under different conditions from 20 to 1000 lux and color temperatures from 2300K to 6500K.
In the tele zoom department, the Samsung engineers have opted for a two-lens approach. The S23 Ultra uses two tele modules with relatively small image sensors and 3x (69mm) and 10x (230mm) zoom factors, respectively. In contrast, most direct competitors, such as the Google Pixel 7 Pro, Huawei Mate 50 Pro and Honor Magic4 Ultimate, use just one tele camera module with a larger image sensor and a higher pixel count.
The results were encouraging, with good levels of detail across most zoom settings. Thanks to the dedicated 10x module, performance was very good at very long range in bright light. However, the S23 Ultra lagged behind the competition at close range, where we would have expected better results, given the primary camera uses a 200MP sensor that should provide excellent digital zooming capabilities.
Overall, the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra was capable of beating the iPhone 14 Pro in the zoom category, thanks to more consistency across the zoom range and much better results at very long range. However, it could not quite match the overall quality of the Huawei Mate 50 Pro or the Honor Magic 4 Ultimate, which delivered better results on most tested ranges. The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra, however, generally had the best results at very long range in bright-light conditions.
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra Zoom Scores vs Ultra-Premium
This graph illustrates the relative scores for the different zoom ranges evaluated. The abscissa is expressed in 35mm equivalent focal length. Zooming-in scores are displayed on the right and Zooming-out scores on the left.
Video Zoom
This graph shows the video detail preservation score in low light, indoor and outdoor conditions when using zoom-in. The level of detail is measured at multiple focal lengths, including those that can directly be chosen via a button in the camera UI. The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra offered consistently higher levels of detail from ultra-wide (14mm/0.5x) to long range (280mm/10x) compared to its predecessor Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon). However, the iPhone 14 Pro was capable of delivering better detail in most conditions.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation video score vs lux levels
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation video score with the level of lux in video. DMC detail preservation score is derived from an AI-based metric trained to evaluate texture and details rendering on a selection of crops of our SBMARK chart.
During our tests, we discovered a small limitation that could probably be fixed with a firmware update. When starting to zoom in from the 0.6x zoom setting (ultra-wide) it was not possible to zoom any further than 2x. From a 1x initial zoom factor, however, it was possible to go up all the way to 10x.
Wide
105
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
Huawei Mate 50 Pro
These tests analyze the performance of the ultra-wide camera at several focal lengths from 12 mm to 20 mm. All image quality attributes are evaluated, with particular attention paid to such artifacts as chromatic aberrations, lens softness, and distortion. Pictures below are an extract of tested scenes.
The S23 Ultra’s ultra-wide camera comes with a 13mm equivalent focal length, offering a wide field of view. In addition, rendering was very good in bright outdoor conditions. Things looked slightly different under indoor lighting and in low light, where noise could become quite intrusive.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Ultra wide

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Noise

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Ultra wide

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Slight noise

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Ultra wide

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Slight noise
Tele
105
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
All image quality attributes are evaluated at focal lengths from approximately 40 mm to 300 mm, with particular attention paid to texture and detail. The score is derived from a number of objective measurements in the lab and perceptual analysis of real-life images.
The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra generally captured good detail at most zoom settings. A boost is noticeable at 230mm, where images are captured at the dedicated 10x module’s native resolution. However, things looked less positive under indoor lighting (100lux) where the tele module’s relatively small image sensor struggled with noise. It’s worth keeping in mind that under 5lux the S23 Ultra does not use its 10x module, most likely to keep noise under control.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score per focal length
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with respect to the full-frame equivalent focal length for different light conditions. The x-axis represents the equivalent focal length measured for each corresponding shooting distance and the y-axis represents the maximum details preservation metric score: higher value means better quality. Large dots correspond to zoom ratio available in the user interface of the camera application.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score per focal length
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with respect to the full-frame equivalent focal length for different light conditions. The x-axis represents the equivalent focal length measured for each corresponding shooting distance and the y-axis represents the maximum details preservation metric score: higher value means better quality. Large dots correspond to zoom ratio available in the user interface of the camera application.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score per focal length
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with respect to the full-frame equivalent focal length for different light conditions. The x-axis represents the equivalent focal length measured for each corresponding shooting distance and the y-axis represents the maximum details preservation metric score: higher value means better quality. Large dots correspond to zoom ratio available in the user interface of the camera application.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score per focal length
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with respect to the full-frame equivalent focal length for different light conditions. The x-axis represents the equivalent focal length measured for each corresponding shooting distance and the y-axis represents the maximum details preservation metric score: higher value means better quality. Large dots correspond to zoom ratio available in the user interface of the camera application.
At close tele zoom range, the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra generally captured good detail, but our testers expected more from the primary camera’s 200MP sensor that should, in theory, enable excellent detail, even when applying a degree of digital zoom.
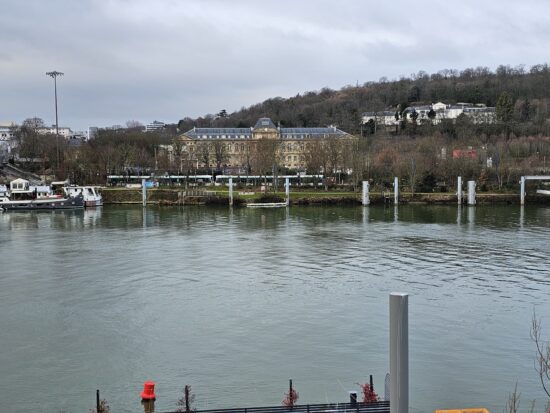

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – 50mm

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Low detail
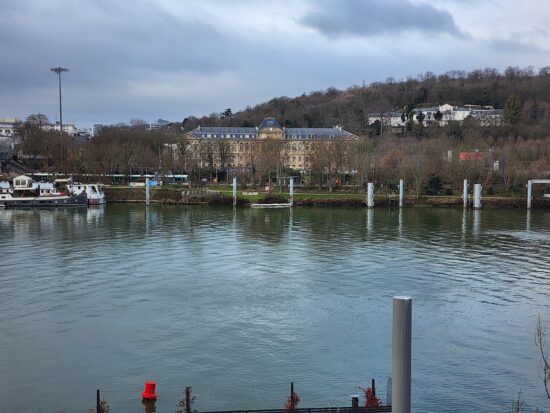

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – 50mm

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Low detail
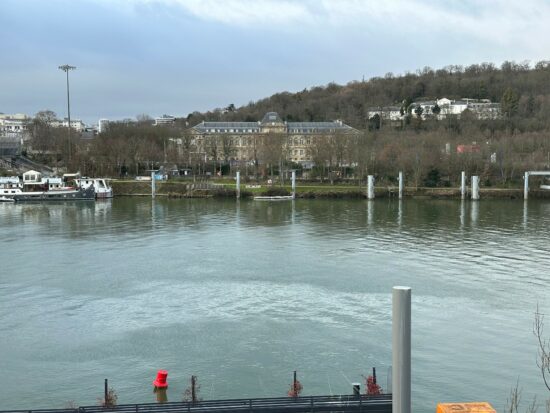

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – 50mm

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Slightly better details
In terms of image detail at close range tele, the Samsung was on par with the best in class, but displayed higher levels of noise.
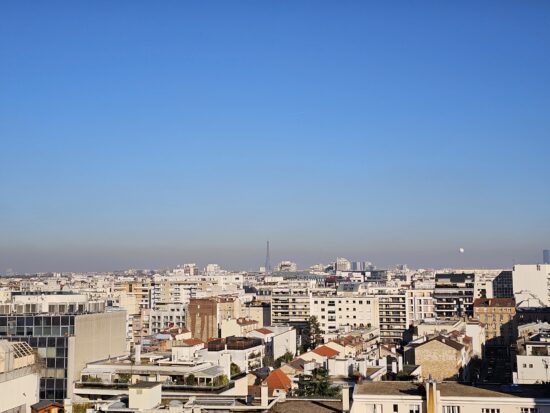

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – 50mm

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Lack of detail, noise
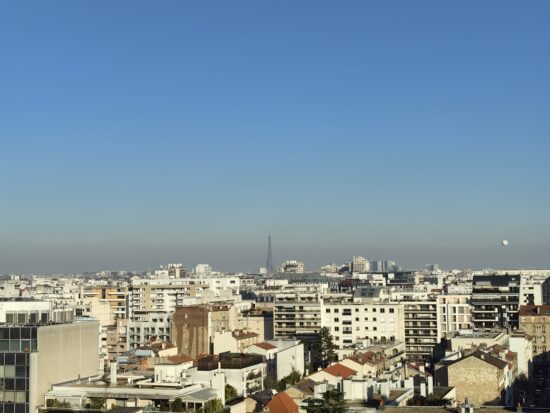

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – 50mm

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – Lack of detail, well controlled noise
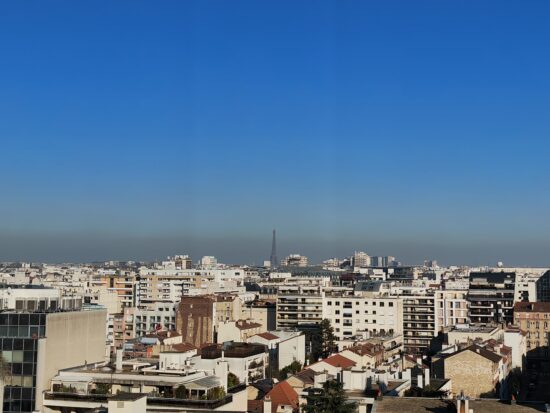

Honor Magic 4 Ultimate – 50mm

Honor Magic 4 Ultimate – Lack of detail, well controlled noise
At medium and long range (approximately 69mm to 230mm equivalent), the Galaxy S23 Ultra was capable of capturing good detail. Noise was noticeable, though, when shooting indoors or in low light. We noticed that the camera sometimes used image fusion when getting closer to the 230mm 10x tele zoom factor. This worked well, with excellent detail at the center of the frame. However, there was also a big drop in detail toward the edges (click on the main thumbnails below to open up the full-size image).
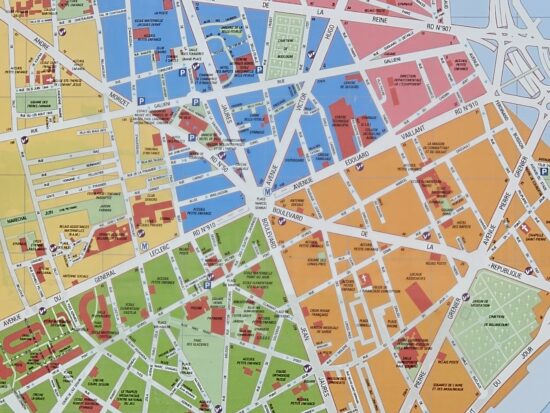
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – 170mm

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Good detail at center but strong corner softness
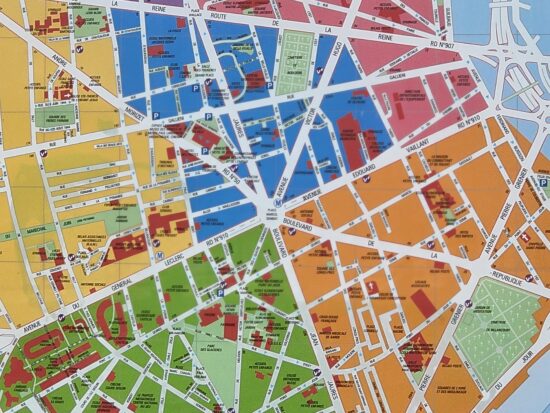
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – 170mm

Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon) – Loss of detail at center, strong corner softness
Apple iPhone 14 Pro – 170mm

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Consistent loss of detail across frame
This said, the fusion algorithms did not always trigger, resulting in slightly disappointing texture and detail rendering, like in these samples that were shot at an 8x tele zoom setting.
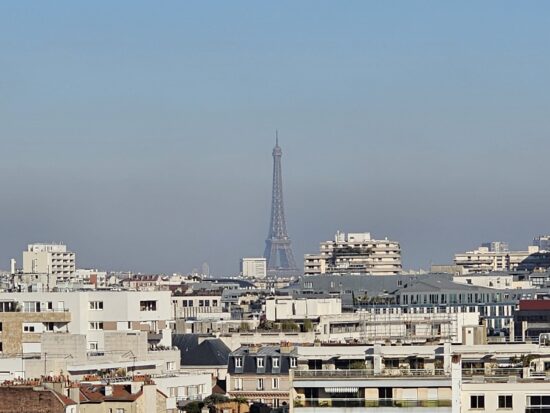

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – 190mm

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Loss of detail, noise
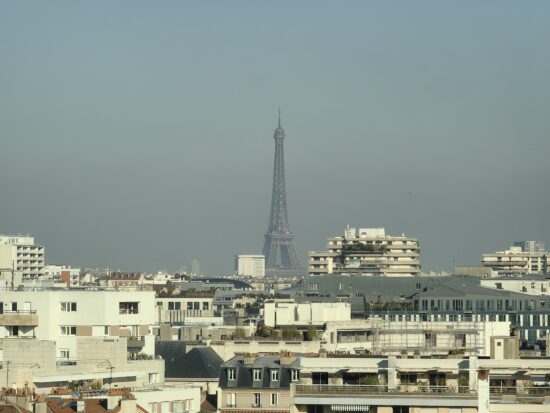

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – 190mm

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – Slight loss of detail, no noise
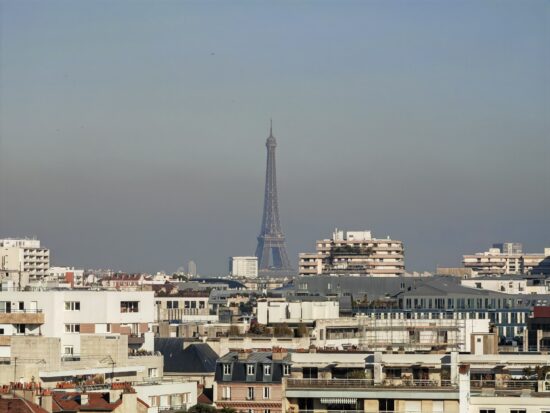

Honor Magic 4 Ultimate – 190mm

Honor Magic 4 Ultimate – Slight loss of detail, no noise
The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra gets the most out of its 10x camera module when shooting in bright light. In such conditions, noise is fairly well under control and the Samsung is ahead of the competition.

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – 230mm

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Fairly good detail
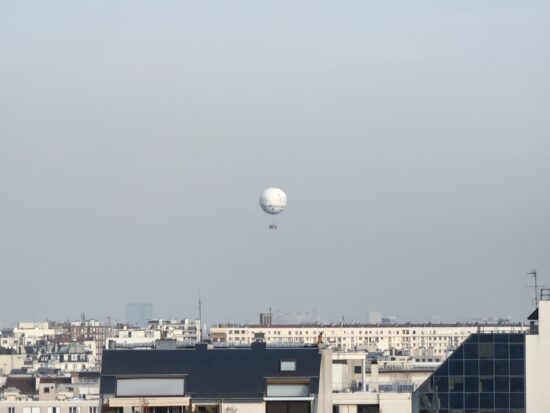

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – 230mm

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – Loss of detail
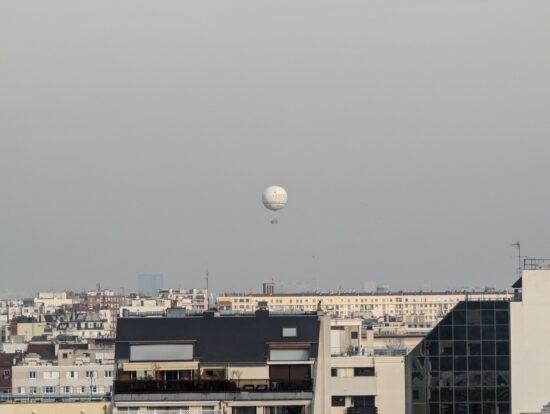

Google Pixel 7 Pro – 230mm

Google Pixel 7 Pro – Fairly good detail
However, in dimmer conditions things change. The relatively small photosites (1.12 microns) of the tele sensor struggled to keep noise down. In this sample scene, the Huawei Mate 50 Pro, which used its much shorter 90mm tele camera, produced an image with better detail and lower noise than the S23 Ultra.
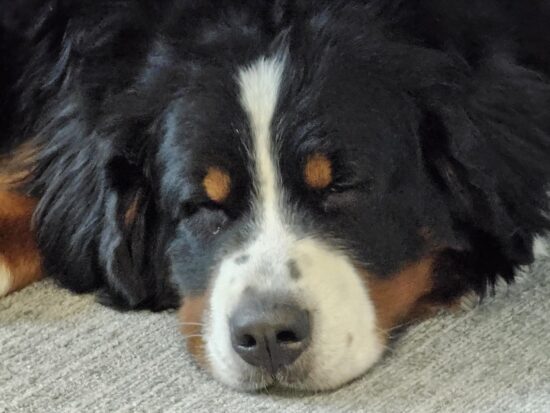

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – 230mm

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – Lack of detail, noise
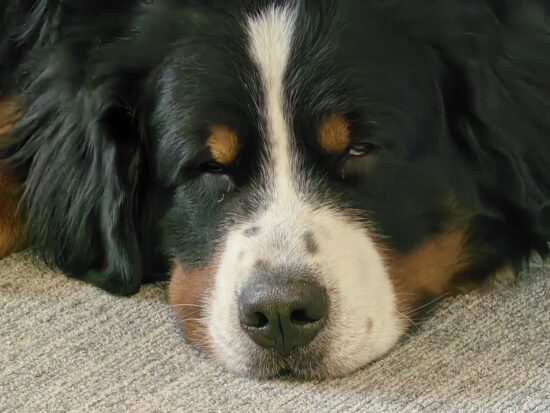

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – 230mm

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – Good detail, low noise
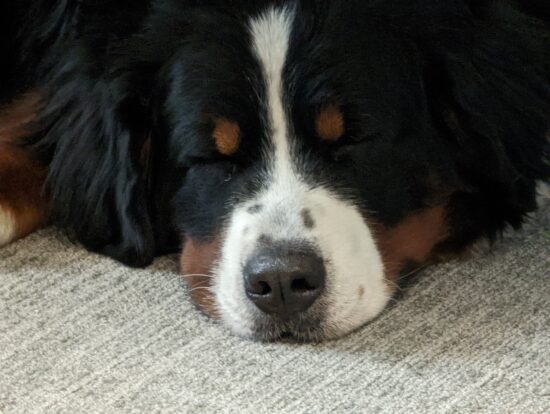

Google Pixel 7 Pro – 230mm

Google Pixel 7 Pro – Lack of detail, noise
At very long range, such as in the 100x sample below, the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra was capable of achieving better detail than the best competitors. However, image quality at this kind of extreme tele zoom factors is generally low on all smartphones.
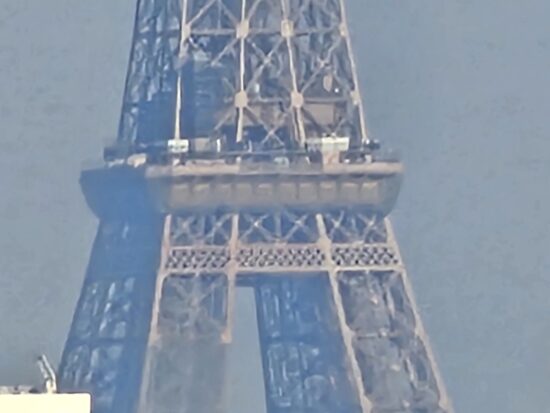

Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra – 100x – Better detail
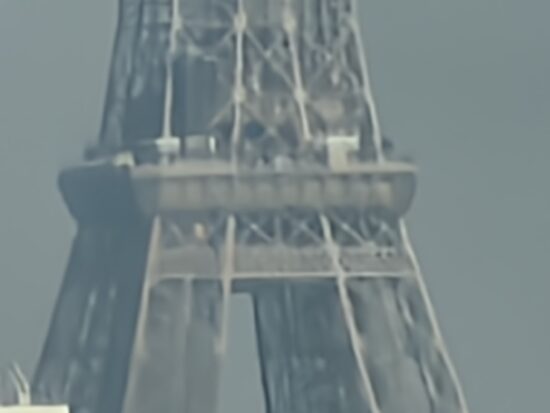

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – 100x – Loss of detail
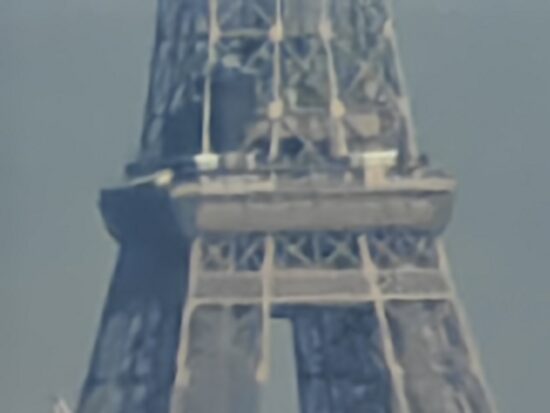

Honor Magic 4 Ultimate – 100x – Loss of detail
Video
137
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
About SBMARK Camera Video tests
SBMARK engineers capture and evaluate more than 2.5 hours of video in controlled lab environments and in natural low-light, indoor and outdoor scenes, using the camera’s default settings. The evaluation consists of visually inspecting natural videos taken in various conditions and running objective measurements on videos of charts recorded in the lab under different conditions from 1 to 1000+ lux and color temperatures from 2,300K to 6,500K.
The S23 Ultra’s video mode was tested at 4k resolution and 60 frames per second, with an auto-fps option activated by default. This option reduces the frame rate automatically when shooting in low light. The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra performed overall well as a video capture device. Autofocus tracking was very good, with a fast and accurate performance ensuring that faces were in focus. In addition, video stabilization was one of the best we have seen to date. In our tests, it was capable of counteracting even strong camera motion in difficult scenarios. Our testers also found white balance and color rendering to be mostly accurate in bright light and when shooting indoors. However, in low light, we observed some white balance instabilities.
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra Video scores vs Ultra-Premium
Video tests analyze the same image quality attributes as for still images, such as exposure, color, texture, or noise, in addition to temporal aspects such as speed, and smoothness and stability of exposure, white balance, and autofocus transitions.
Exposure
103
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Exposure tests evaluate the brightness of the main subject and the dynamic range, eg. the ability to render visible details in both bright and dark areas of the image. Stability and temporal adaption of the exposure are also analyzed.
Video clips captured on the S23 Ultra featured a wide dynamic range in bright light, recording good detail in both highlight and shadow areas of the frame. However, our testers observed some tone compression in the highlights when filming high-contrast scenes. Exposure transitions were quite smooth, despite the occasional overshoot.
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
When recording in low light, we observed shadow clipping and a loss of detail, especially on dark skin tones.
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
Color
104
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Image-quality color analysis looks at color rendering, skin-tone rendering, white balance, color shading, stability of the white balance and its adaption when light is changing.
Color rendering was nice in bright outdoor conditions, especially on skin tones. However, we also observed a blue color cast on some occasions.
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
In low light, our testers found skin tones to look unnatural in some scenes. We also noticed some color casts.
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
Autofocus
110
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
The Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra video autofocus provided excellent performance in most conditions. Only in very low light could focus transitions have been sometimes faster and smoother (visible at around 9s in this sample). In this clip the iPhone provided fast and hardly visible focus transitions.
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
Texture
108
Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra
Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra
Texture tests analyze the level of details and texture of the real-life videos as well as the videos of charts recorded in the lab. Natural videos recordings are visually evaluated, with particular attention paid to the level of details in the bright and areas as well as in the dark. Objective measurements are performed of images of charts taken in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux. The charts used are the SBMARK chart (DMC) and Dead Leaves chart.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation video score vs lux levels
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation video score with the level of lux in video. DMC detail preservation score is derived from an AI-based metric trained to evaluate texture and details rendering on a selection of crops of our SBMARK chart.
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra video footage offered good detail, with a lot of fine texture, especially when recording in daylight conditions. In low light, detail dropped slightly, as you would expect, especially in low contrast areas of the frame, but detail rendering remained overall nice.
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
Noise
111
Samsung Galaxy A23 5G
Samsung Galaxy A23 5G
Noise tests analyze various attributes of noise such as intensity, chromaticity, grain, structure, temporal aspects on real-life video recording as well as videos of charts taken in the lab. Natural videos are visually evaluated, with particular attention paid to the noise in the dark areas and high dynamic range conditions. Objective measurements are performed on the videos of charts recorded in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux. The chart used is the SBMARK visual noise chart.
Spatial visual noise evolution with the illuminance level
This graph shows the evolution of spatial visual noise with the level of lux. Spatial visual noise is measured on the visual noise chart in the video noise setup. SBMARK visual noise measurement is derived from ISO15739 standard.
Temporal visual noise evolution with the illuminance level
This graph shows the evolution of temporal visual noise with the level of lux. Temporal visual noise is measured on the visual noise chart in the video noise setup.
In video mode, the ability to control noise is one of the biggest strengths of the Samsung. Both temporal and spatial noise were very well kept at bay. Again, things changed slightly under low light conditions, where luminance noise become noticeable on moving subjects and in the shadow areas.
Stabilization
114
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Stabilization evaluation tests the ability of the device to stabilize footage thanks to software or hardware technologies such as OIS, EIS, or any others means. The evaluation looks at residual motion, smoothness, jello artifacts and residual motion blur on walk and run use cases in various lighting conditions. The video below is an extract from one of the tested scenes.
Video stabilization worked reliably in our tests, counteracting even walking and running motion nicely. Only a little camera motion and some frameshift effect were sometimes noticeable. The iPhone was even slightly better, thanks to more effective stabilization of running motion.
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)
Artifacts
77
Xiaomi 12S Ultra
Xiaomi 12S Ultra
Artifacts are evaluated with MTF and ringing measurements on the SFR chart in the lab as well as frame-rate measurements using the LED Universal Timer. Natural videos are visually evaluated by paying particular attention to artifacts such as aliasing, quantization, blocking, and hue shift, among others. The more severe and the more frequent the artifact, the higher the point deduction from the score. The main artifacts and corresponding point loss are listed below.
Overall, the most common video artifacts were quite well under control on the Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra, but our testers noticed some slight artifacts, including aliasing, moiré, color quantization, and ringing. Thanks to the 60fps frame rate in bright light, motion was pleasantly smooth.
Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra (Snapdragon)







Start a new Thread