We put the Huawei Mate 50 Pro through our rigorous SBMARK Camera test suite to measure its performance in photo, video, and zoom quality from an end-user perspective. This article breaks down how the device fared in a variety of tests and several common use cases and is intended to highlight the most important results of our testing with an extract of the captured data.
Overview
Key camera specifications:
- Primary: 50MP sensor, 24mm equivalent lens with f/1.4 – f/4.0 adjustable aperture, OIS
- Ultra-wide: 13MP sensor, 13mm equivalent f/2.2-aperture lens
- Tele: 64MP, 90mm equivalent f/3.5-aperture lens, OIS
Pros
- Wide dynamic range in both photo and video
- High level of image detail
- Very well-controlled noise in photo
- Extended depth of field on group pictures in bright light conditions
- Good detail preservation across all zoom ranges
- Pleasant simulated bokeh effect
- Generally fast and accurate autofocus in photo and video
- Pleasant colors in bright light conditions
- Residual motion is well-controlled in video mode
Cons
- Slight white balance casts that are sometimes visible
- Differences between preview and capture that are often visible on difficult scenes
- Sometimes slightly slow capture on difficult scenes
- Sharpness differences between frames are often visible in video
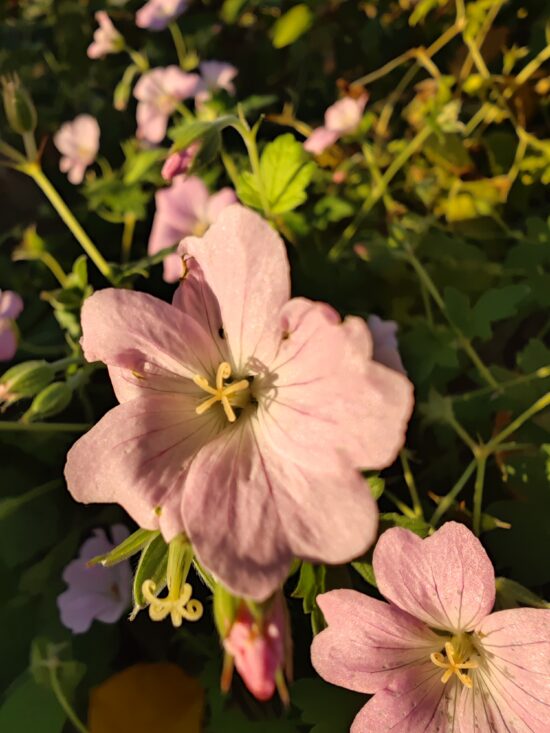
With a SBMARK Camera score of 149, the Huawei Mate 50 Pro is the new No. 1 in our smartphone camera ranking. It also achieved the best Photo score to date, thanks to excellent results in the exposure, focus, and texture/noise categories.
The autofocus score benefited a lot from the new and innovative adjustable aperture, which allows for the optimization of the depth of field in a scene. An adjustable aperture is especially useful, for example, in group portraits. As smartphone image sensors have become bigger, the effect has been a reduced depth of field, which makes it more difficult to keep all subjects in focus if they are not in the same focus plane. The Huawei system uses an embedded diaphragm that allows for adjustment from f/1.4 to f/4.0, so, depending on the scene, the camera can either prioritize light capture (in low light), maximize depth of field, or pick a more balanced setting between the two extremes. We last saw a similar feature on the Samsung Galaxy Note 10 series with its duo aperture, but it’s still quite uncommon, and the Samsung feature does not lead to the same results.
Zoom quality is a strong point of the device, thanks to a combination of three camera modules with super-resolution and fusion algorithms. The result is good detail preservation from ultra-wide to long-range tele. Overall, the Mate 50 Pro ranks second for Zoom, just behind the Honor Magic4 Ultimate, which offers slightly better detail at medium-range tele.
For video, the Mate 50 Pro was tested at 4K resolution and 30 frames per second, with Vivid HDR mode enabled. Vivid HDR is a new HDR video format and already supported by phones and some TVs (http://www.theuwa.com/terminal-certify). Overall, the Mate 50 Pro was not quite as outstanding for video as it was for still images and only ranks 7th, lower than its direct rivals Google Pixel 7 Pro and the latest Apple iPhones. Exposure was the main strength in video, with accurate target exposure and a wide dynamic range in bright light and indoors. However, the Huawei Mate 50 Pro somewhat lagged behind the best in class in terms of texture/noise compromise, especially in low light.
Friends & Family
Things look different for our new Friends & Family use case score. Here, the Mate 50 Pro scored one point higher than the Google Pixel 7 Pro and two points higher than the Apple iPhone 14 Pro. As mentioned above, the new adjustable aperture gave the Huawei phone a real advantage over the competition for group shots. Skin tones were mostly well rendered, but pink or orange shifts could become visible under specific conditions. Our testers also found the Mate 50 Pro to be a little less capable of capturing the decisive moment than some of its rivals. Especially in low light, the Pixel 7 Pro was faster at capturing an image and better at avoiding motion blur.
It’s worth mentioning that the Mate 50 Pro does not come with the Leica imaging system found on the P50 Pro. Instead, it is equipped with Huawei’s own XMAGE system, which lets the user choose from three image-rendering presets: Vivid, Bright, and Original. Vivid increases contrast, Bright increases brightness while balancing the exposure, and Original attempts to render colors the same way as they are seen by the user’s eyes. All our testing was done in Original mode.

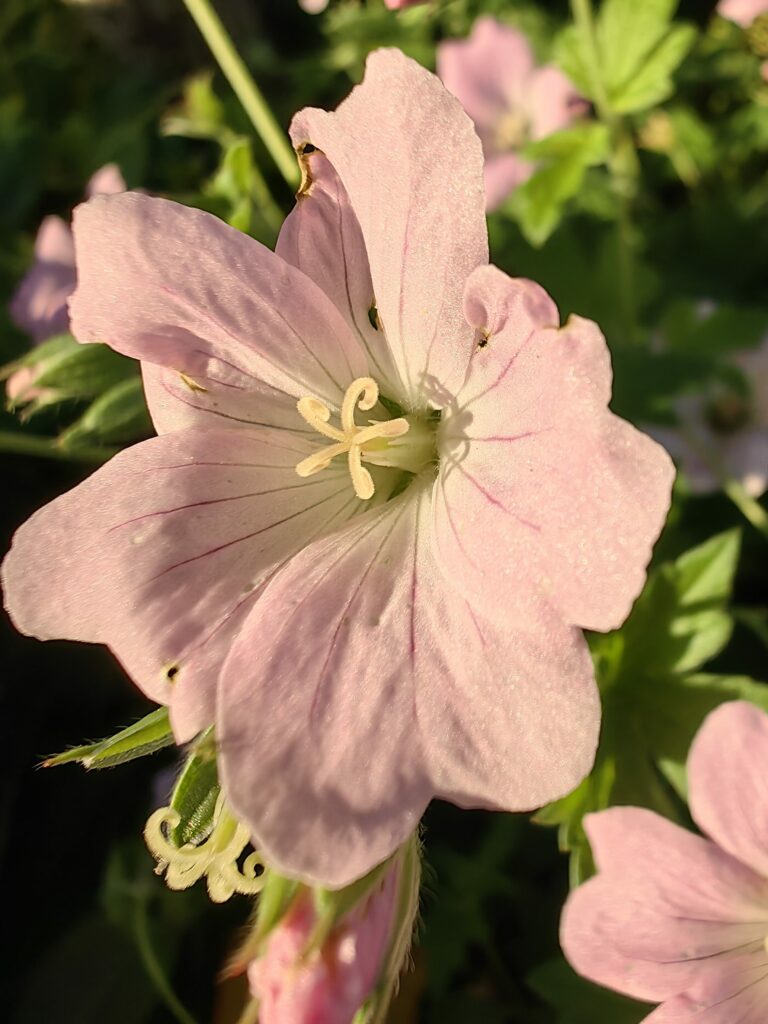
Huawei Mate 50 Pro – pleasantly natural color; wide depth of field keeps all subjects in focus
Lowlight
When tested under dim conditions, the Mate 50 Pro provided sharp and quite natural detail, as well as a very wide dynamic range, which overall resulted in the best low-light score we have seen to date. Image rendering was very well balanced, with nice and vivid colors as well as pleasant contrast. It appears that the Huawei engineers tried to render the mood of low-light scenes by allowing a slightly warm color cast. In low light, the camera kept the aperture wide open at f/1.4 in order to capture as much light as possible.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – Pleasant contrast and close to fidelity white balance

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – Natural details rendering

Google Pixel 7 Pro – Blue white balance

Google Pixel 7 Pro – Strong autofocus failure

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – White balance is slightly yellow green

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – Oversharped details
When using the tele zoom in low light, the Mate 50 Pro also managed to preserve more details and kept noise levels lower than its rivals at most zoom settings.
Low-light video quality on the other hand was lower than on the direct competitors, especially when compared to the iPhone 14 Pro. Texture artifacts and quite strong noise were the most noticeable drawbacks when recording video in dim conditions.
Huawei Mate 50 Pro Camera Scores vs Ultra-Premium
This graph compares SBMARK photo, zoom and video scores between the tested device and references. Average and maximum scores of the price segment are also indicated. Average and maximum scores for each price segment are computed based on the SBMARK database of devices tested.
Test summary
About SBMARK Camera tests: SBMARK’s Camera evaluations take place in laboratories and in real-world situations using a wide variety of subjects. The scores rely on objective tests for which the results are calculated directly by measurement software on our laboratory setups, and on perceptual tests in which a sophisticated set of metrics allow a panel of image experts to compare aspects of image quality that require human judgment. Testing a smartphone involves a team of engineers and technicians for about a week. Photo, Zoom, and Video quality are scored separately and then combined into an Overall score for comparison among the cameras in different devices. For more information about the SBMARK Camera protocol, click here. More details on smartphone camera scores are available here. The following section gathers key elements of SBMARK’s exhaustive tests and analyses. Full performance evaluations are available upon request. Please contact us on how to receive a full report.
About SBMARK Camera Photo tests
For scoring and analysis, SBMARK engineers capture and evaluate more than 2,600 test images both in controlled lab environments and in outdoor, indoor and low-light natural scenes, using the camera’s default settings. The photo protocol is designed to take into account the main use cases and is based on typical shooting scenarios, such as portraits, family, and landscape photography. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting images Cons a reference of natural scenes, and by running objective measurements on images of charts captured in the lab under different lighting conditions from 1 to 1,000+ lux and color temperatures from 2,300K to 6,500K.
In photo, the Mate 50 Pro received the best overall score to date, thanks to excellent results in exposure, autofocus, and texture/noise. It generally provided very pleasant rendering, even in difficult conditions such as low light or high dynamic range scenes.
Huawei Mate 50 Pro Photo scores vs Ultra-Premium
The photo tests analyze image quality attributes such as exposure, color, texture, and noise in various light conditions. Autofocus performances and the presence of artifacts on all images captured in controlled lab conditions and in real-life images are also evaluated. All these attributes have a significant impact on the final quality of the images captured with the tested device and can help to understand the camera’s main strengths and weaknesses.
Close-Up
Close-up is the third new use case score introduced with SBMARK Camera version 5. It evaluates the camera’s ability to capture detail at subject distances below 10cm and magnifications as close as possible to 1:1.
In its macro mode, the Mate 50 Pro used the ultra-wide camera, with convincing results. Close-up shots tended to come with accurate exposure and nice color. Fine detail was rendered much better than on the Xiaomi 12S Ultra but lagged slightly behind the iPhone 14 Pro. Note that these samples were captured at the minimum focus distance for each device. As seen below, the Mate 50 Pro and the iPhone 14 Pro allow you to get much closer than the Xiaomi.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – macro

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – good detail


Xiaomi 12S Ultra – lack of detail

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – macro

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – very good detail
Exposure is one of the key attributes for technically good pictures. The main attribute evaluated is the brightness of the main subject through various use cases such as landscape, portrait, or still life. Other factors evaluated are the contrast and the dynamic range, eg. the ability to render visible details in both bright and dark areas of the image. Repeatability is also important because it demonstrates the camera’s ability to provide the same rendering when shooting several images of the same scene.
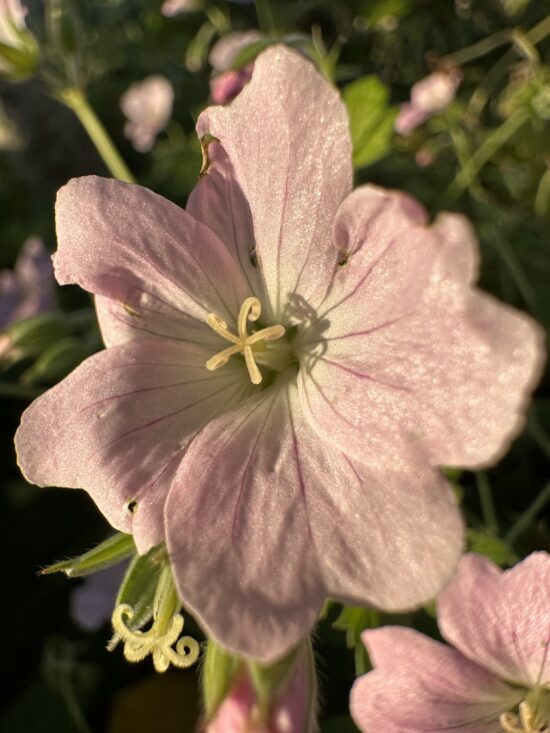
The Mate 50 Pro follows in the footsteps of previous Huawei devices and delivered class-leading exposure. Target exposure tended to be spot on, and a wide dynamic range ensured good detail in both the highlight and shadow areas of the frame. Compared to some of its main competitors, the Mate 50 Pro was also capable of creating nice contrast, but in strongly backlit scenes, this could come at the expense of a halo effect around the subject.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – accurate face exposure, wide dynamic range

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – slight underexposure on the face, highlight clipping

Honor Magic 4 Ultimate – accurate face exposure, wide dynamic range
The Mate 50 Pro achieved the high score in our database for exposure, better than the Honor Magic4 Ultimate by one point. This was thanks to natural and pleasant contrast, as well as accurate target exposure and wide dynamic range in low light.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – low light exposure and contrast

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – accurate face exposure and pleasant contrast

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – low light exposure and contrast

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – Contrast is slightly too high and clipping is visible
Color
116
Google Pixel 7 Pro
Google Pixel 7 Pro
Color is one of the key attributes for technically good pictures. The image quality attributes analyzed are skin-tone rendering, white balance, color shading, and repeatability. For color and skin tone rendering, we penalize unnatural colors but we respect a manufacturer’s choice of color signature.
The Mate 50 Pro delivered nice colors and accurate white balance, especially when capturing scenes with a low dynamic range.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – close color fidelity and white balance
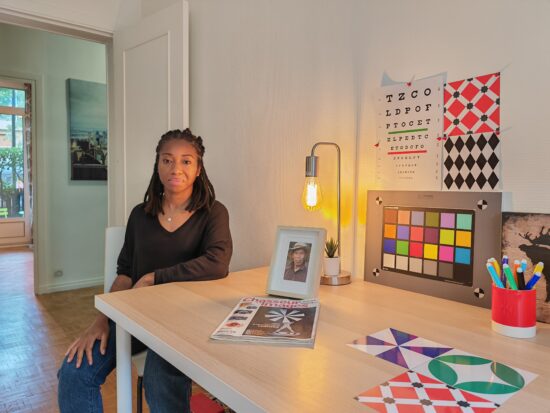

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – close color fidelity and white balance but strong quantification in highlights

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – white balance is slightly too blue in the background
However, green casts under indoor conditions and blue casts in bright outdoor light meant it could not quite match the color performance of the Apple iPhone 14 Pro and the Google Pixel 7 Pro. Our testers also found the skin tone rendering to be slightly off in some instances, with too much saturation on fair skin tones.

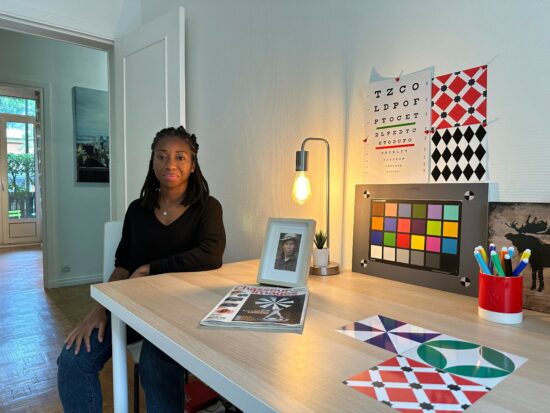
Huawei Mate 50 Pro – nice color overall but skin tones slightly orange

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – slightly desaturated skin tones
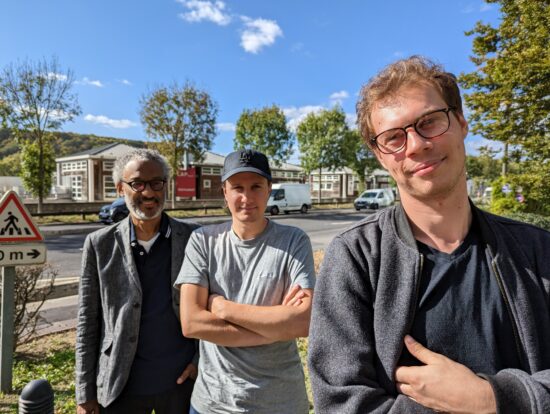

Google Pixel 7 Pro – well-balanced color and skin tones
Autofocus tests concentrate on focus accuracy, focus repeatability, shooting time delay, and depth of field. Shooting delay is the difference between the time the user presses the capture button and the time the image is actually taken. It includes focusing speed and the capability of the device to capture images at the right time, what is called ‘zero shutter lag’ capability. Even if a shallow depth of field can be pleasant for a single subject portrait or close-up shot, it can also be a problem in some specific conditions such as group portraits; Both situations are tested. Focus accuracy is also evaluated in all the real-life images taken, from infinity to close-up objects and in low light to outdoor conditions.
The adjustable aperture is arguably the Mate 50 Pro’s most important innovation. It allows the photographer to choose between a very wide depth of field at f/4 or maximized light-capturing capability at f/1.4. In default photo mode, the camera never appeared to use apertures smaller than f/2.8. In this sample, the camera used f/2.8, which is enough to keep all subjects in focus, unlike the iPhone 14 Pro and Magic4 Ultimate.
In order to use f/4, Pro Mode needs to be activated, which allows the user to choose manually from 10 aperture settings. This offers much greater flexibility in terms of depth of field than any other smartphone camera available today.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – depth of field

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – both faces in focus, thanks f/2.8 aperture

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – depth of field

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – background subject slightly out of focus

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – depth of field

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – background subject slightly out of focus
In our tests, the Mate 50 Pro switched from f/2.0 to f/2.8 when it detected more than one person in the scene, in order to extend the depth of field. This can be seen in the series of images below. This way, for a single portrait shot, the limited depth of field of the f/2 aperture was used to create a mild bokeh effect and to isolate the subject from the background. With more people in the scene, the priority switched to keeping all subjects in focus, and the camera used f/2.8. In low light, this strategy changed, and the camera would generally stick to f/1.4 to allow for maximum light capture.
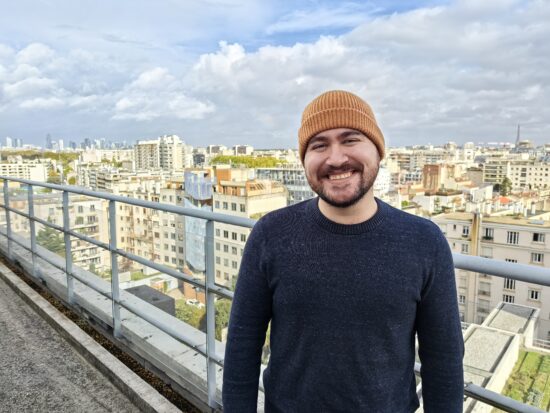

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – one person, f/2.0

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – blur on background, limited depth of field
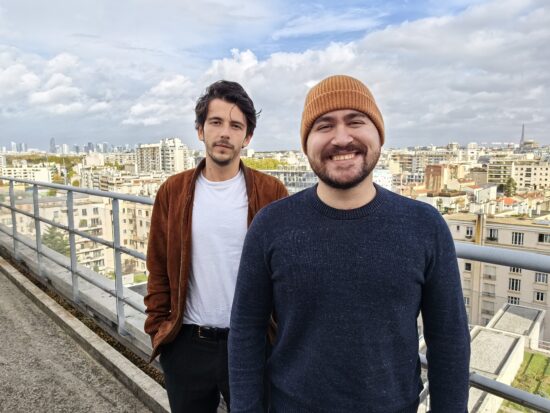

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – two people, f/2.8

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – no blur on background, wide depth of field

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – three people, f/2.8

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – no blur on background, wide depth of field
The Mate 50 Pro autofocus system delivered accurate focus and was very consistent in doing so. On the downside, it would on occasions be a little slow, which meant missing the exact moment intended for capture, especially in high-contrast situations. In this scene, the shutter was triggered right at the moment the person kicked the ball. The Mate 50 Pro image was captured a fraction of a second too late. The Pixel 7 Pro did a better job at capturing the right moment.
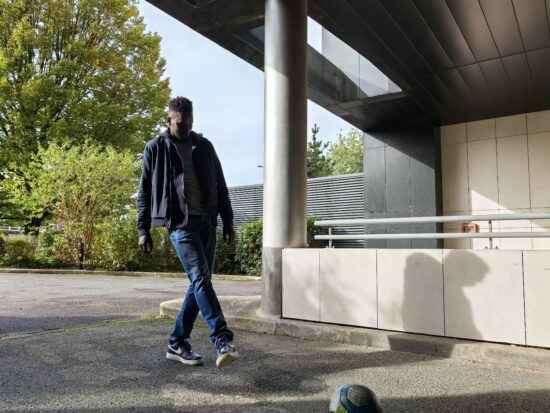

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – image captured slightly late

Google Pixel 7 Pro – faster capture
In scenes with a low dynamic range, the Mate 50 Pro managed to capture images faster providing a real zero-shutter lag, unlike some other flagship phones, such as the Xiaomi 12S Ultra or Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra.
Autofocus irregularity and speed: 20Lux Δ0EV Tungsten Handheld
This graph illustrates focus accuracy and speed and also zero shutter lag capability by showing the edge acutance versus the shooting time measured on the AFHDR setup on a series of pictures. All pictures were taken at 20Lux with Tungsten illuminant, 500ms after the defocus. The edge acutance is measured on the four edges of the Dead Leaves chart, and the shooting time is measured on the LED Universal Timer.
Autofocus irregularity and speed: 1000Lux Δ0EV Daylight Handheld
This graph illustrates focus accuracy and speed and also zero shutter lag capability by showing the edge acutance versus the shooting time measured on the AFHDR setup on a series of pictures. All pictures were taken at 1000Lux with Daylight illuminant, 500ms after the defocus. The edge acutance is measured on the four edges of the Dead Leaves chart, and the shooting time is measured on the LED Universal Timer.
Texture
107
Oppo Find X5
Oppo Find X5
Texture tests analyze the level of details and the texture of subjects in the images taken in the lab as well as in real-life scenarios. For natural shots, particular attention is paid to the level of details in the bright and dark areas of the image. Objective measurements are performed on chart images taken in various lighting conditions from 1 to 1000 lux and different kinds of dynamic range conditions. The charts used are the proprietary SBMARK chart (DMC) and the Dead Leaves chart.
The level of detail in the Mate 50 Pro images was in line with the flagship competitors in its class.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score vs lux levels for tripod and handheld conditions
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with the level of lux, for two holding conditions. DMC detail preservation score is derived from an AI-based metric trained to evaluate texture and details rendering on a selection of crops of our SBMARK chart.
Detail was preserved well down to low light. In this sample, detail was on a similar level as the Honor Magic4 Ultimate, and better than on the iPhone, which showed some quite unnatural detail with ringing effects.
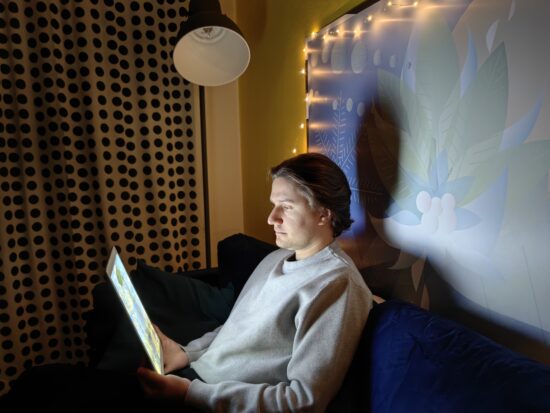

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – low light detail

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – good detail
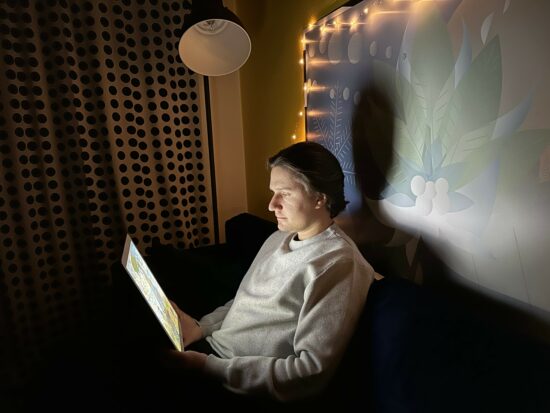

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – low light detail

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – quite unnatural detail
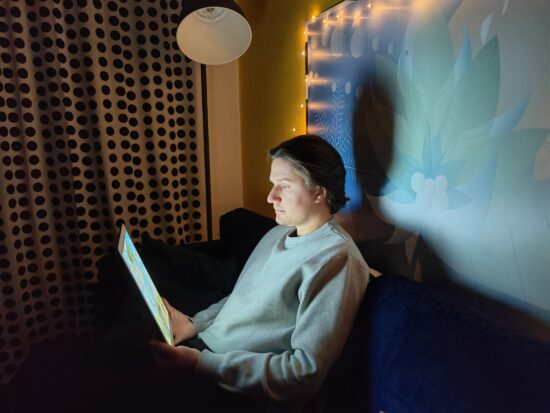

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – low light detail

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – good detail
Noise
113
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
Noise tests analyze various attributes of noise such as intensity, chromaticity, grain, structure on real-life images as well as images of charts taken in the lab. For natural images, particular attention is paid to the noise on faces, landscapes, but also on dark areas and high dynamic range conditions. Noise on moving objects is also evaluated on natural images. Objective measurements are performed on images of charts taken in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux and different kinds of dynamic range conditions. The chart used is the Dead Leaves chart and the standardized measurement such as Visual Noise derived from ISO 15739.
In this graph, we see visual noise measurements from our lab in different light levels for the Mate 50 Pro and two competitors. On the Mate 50 Pro, noise was generally well under control at all light levels.
Visual noise evolution with illuminance levels in handheld condition
This graph shows the evolution of visual noise metric with the level of lux in handheld condition. The visual noise metric is the mean of visual noise measurement on all patches of the Dead Leaves chart in the AFHDR setup. SBMARK visual noise measurement is derived from ISO15739 standard.
Huawei’s noise reduction strategy remains unchanged from previous models. There was pretty much no fine luminance noise noticeable in any conditions. This was quite different to the Pixel 7 Pro, and especially the iPhone 14 Pro, which both allowed some fine noise in their images. Overall noise is very well under control on the Huawei Mate 50 Pro. Only some chroma noise “blobs” could be noticeable, resulting in pinkish image areas, especially in low light.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – low light noise

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – no noise

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – low light noise

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – visible noise

Google Pixel 7 Pro – low light noise

Google Pixel 7 Pro – very slight chromatic noise
Artifacts
74
Google Pixel 6
Google Pixel 6
The artifacts evaluation looks at lens shading, chromatic aberrations, geometrical distortion, edges ringing, halos, ghosting, quantization, unexpected color hue shifts, among others type of possible unnatural effects on photos. The more severe and the more frequent the artifact, the higher the point deduction on the score. The main artifacts observed and corresponding point loss are listed below.
Main photo artifacts penalties
The most common image artifacts were generally well handled by the Mate 50 Pro. However, halos and color quantification around highlight in low-light scenes were quite intrusive.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – artifacts

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – color quantification near highlights
Bokeh is tested in one dedicated mode, usually portrait or aperture mode, and analyzed by visually inspecting all the images captured in the lab and in natural conditions. The goal is to reproduce portrait photography comparable to one taken with a DLSR and a wide aperture. The main image quality attributes paid attention to are depth estimation, artifacts, blur gradient, and the shape of the bokeh blur spotlights. Portrait image quality attributes (exposure, color, texture) are also taken into account.
The Mate 50 Pro was the best device for bokeh that we have tested to date. A high-resolution depth map allowed for precise isolation of the subject from the background. Foreground blur looked realistic, too, and in combination with the nice spotlight rendering, it made the Mate 50 Pro bokeh images hard to distinguish from an image taken with a DSLR and large aperture lens.
When looking at the image in detail, some slight depth estimation artifacts became visible, but the Huawei was better than most rivals in this respect. It was also obvious that at default settings, the Huawei applied much stronger blur than the iPhone.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – bokeh mode

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – good subject isolation

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – bokeh mode

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – good subject isolation

Google Pixel 7 Pro – bokeh mode

Google Pixel 7 Pro – subject isolation failure
Preview
63
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Preview tests analyze the image quality of the camera app’s preview of the image, with particular attention paid to the difference between the capture and the preview, especially regarding dynamic range and the application of the bokeh effect. Also evaluated is the smoothness of the exposure, color and focus adaptation when zooming from the minimal to the maximal zoom factor available. The preview frame rate is measured using the LED Universal Timer.
In terms of image preview on the display, the Mate 50 Pro showed improvement over the P50 Pro, but it still could not match the iPhone 14 Pro, which managed a very similar image between preview and capture, especially in terms of exposure.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – preview – significant difference to capture in terms of highlight retention
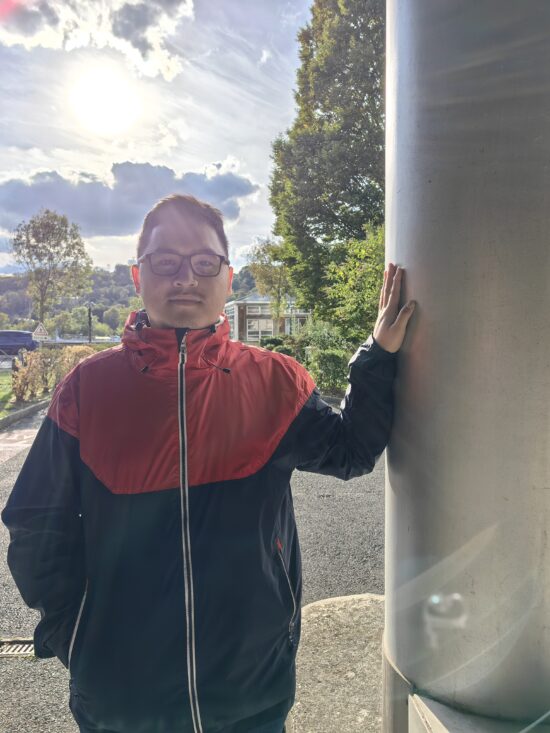

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – capture

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – preview – similar dynamic range as capture
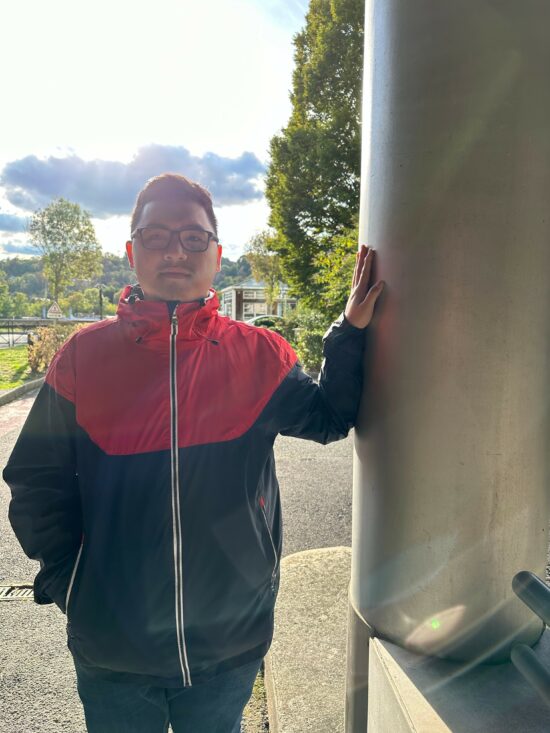

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – capture
Zoom
148
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
About SBMARK Camera Zoom tests
SBMARK engineers capture and evaluate over 400 test images in controlled lab environments and in outdoor, indoor, and low-light natural scenes, using the camera’s default settings and pinch zoom at various zoom factors from ultra wide to very long-range zoom. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting the images Cons a reference of natural scenes, and by running objective measurements of chart mages captured in the lab under different conditions from 20 to 1000 lux and color temperatures from 2300K to 6500K.
The Mate 50 Pro offered very high image quality across almost the entire zoom range. Target exposure was usually accurate, with a wide dynamic range However, slight instabilities could be noticeable across a series of consecutive shots. In the Zoom category, the Mate 50 Pro placed second, behind the Honor Magic4 Ultimate.
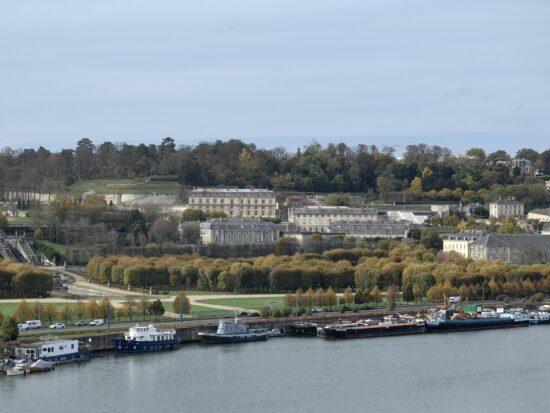

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – good detail with the tele camera
Huawei Mate 50 Pro Zoom Scores vs Ultra-Premium
This graph illustrates the relative scores for the different zoom ranges evaluated. The abscissa is expressed in 35mm equivalent focal length. Zooming-in scores are displayed on the right and Zooming-out scores on the left.
These tests analyze the performance of the ultra-wide camera at several focal lengths from 12 mm to 20 mm. All image quality attributes are evaluated, with particular attention paid to such artifacts as chromatic aberrations, lens softness, and distortion. Pictures below are an extract of tested scenes.
The Mate 50 Pro comes with a 13mm equivalent ultra-wide camera, which offers a wide field of view as well as very good image results with generally pleasant rendering. The device manages generally to provide high texture/noise tradeoff with regards to the competitors, with free-of-noise rendering even down to low light. Optical distortion is very well compensated for.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – ultra-wide

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – good detail

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – ultra-wide

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – good detail but ringing

Xiaomi 12S Ultra – ultra-wide

Xiaomi 12S Ultra – fairly good detail but corner softness
Tele
110
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
Honor Magic4 Ultimate
All image quality attributes are evaluated at focal lengths from approximately 40 mm to 300 mm, with particular attention paid to texture and detail. The score is derived from a number of objective measurements in the lab and perceptual analysis of real-life images.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score per focal length
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with respect to the full-frame equivalent focal length for different light conditions. The x-axis represents the equivalent focal length measured for each corresponding shooting distance and the y-axis represents the maximum details preservation metric score: higher value means better quality. Large dots correspond to zoom ratio available in the user interface of the camera application.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score per focal length
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with respect to the full-frame equivalent focal length for different light conditions. The x-axis represents the equivalent focal length measured for each corresponding shooting distance and the y-axis represents the maximum details preservation metric score: higher value means better quality. Large dots correspond to zoom ratio available in the user interface of the camera application.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score per focal length
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with respect to the full-frame equivalent focal length for different light conditions. The x-axis represents the equivalent focal length measured for each corresponding shooting distance and the y-axis represents the maximum details preservation metric score: higher value means better quality. Large dots correspond to zoom ratio available in the user interface of the camera application.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation score per focal length
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation score with respect to the full-frame equivalent focal length for different light conditions. The x-axis represents the equivalent focal length measured for each corresponding shooting distance and the y-axis represents the maximum details preservation metric score: higher value means better quality. Large dots correspond to zoom ratio available in the user interface of the camera application.
At close range tele (40mm to 70mm), the Mate 50 Pro offered impressively natural rendering at the center of the frame, with good fine detail as well as a wide dynamic range and nice colors. However, there might be a loss of sharpness around the edges of the image, due to fusion algorithms.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – close range tele

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – good detail at 2x tele, slight blue cast

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – close range tele

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – lack of detail

Xiaomi 12S Ultra – close range tele

Xiaomi 12S Ultra – lack of detail
At medium range tele, focus issues became noticeable, and the level of detail was generally very slightly lower than on the Honor Magic4 Ultimate. However, the very low noise level continued to impress, no matter the tele zoom setting.
Huawei Mate 50 Pro – medium range tele

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – good detail

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – medium range tele

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – noise and fairly low level of detail
Honor Magic4 Ultimate – medium range tele

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – good detail, slightly more sharpness than the Mate 50 Pro
Video
141
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
About SBMARK Camera Video tests
SBMARK engineers capture and evaluate more than 2.5 hours of video in controlled lab environments and in natural low-light, indoor and outdoor scenes, using the camera’s default settings. The evaluation consists of visually inspecting natural videos taken in various conditions and running objective measurements on videos of charts recorded in the lab under different conditions from 1 to 1000+ lux and color temperatures from 2,300K to 6,500K.
Mate 50 Pro video was tested at 4K resolution and 30 frames per second. This was the first SBMARK Camera test for which Vivid HDR mode had been activated. HDR formats have become more commonplace for both recording and display over the past few years. Apple has been using the Dolby Vision format since the iPhone 12 series. Some other manufacturers, for example, Samsung, support the HDR10+ format.
Please note that YouTube only displays the original HDR rendering if videos are watched on a compatible HDR screen. Otherwise, a compressed SDR video is displayed.
Huawei Mate 50 Pro Video scores vs Ultra-Premium
Video tests analyze the same image quality attributes as for still images, such as exposure, color, texture, or noise, in addition to temporal aspects such as speed, and smoothness and stability of exposure, white balance, and autofocus transitions.
Exposure
110
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Exposure tests evaluate the brightness of the main subject and the dynamic range, eg. the ability to render visible details in both bright and dark areas of the image. Stability and temporal adaption of the exposure are also analyzed.
The Mate 50 Pro did very well for video exposure, with accurate face exposure, fast and accurate exposure adaptation, and a wide dynamic range as visible below. The video frames below from the iPhone 14 Pro and Mate 50 Pro were created by converting the devices’ 10-bit video frames into 8-bit frames, using a standardized tone-mapping curve, which to some extent is representative of the perceived rendering of an HDR monitor. Note that the overall exposure of these images appears darker than when viewed on an HDR monitor, and that face exposure is acceptable in both images. The iPhone 14 Pro generally has a slightly wider dynamic range, allowing for better highlight recovery in the scene below.

Huawei Mate 50 Pro – slight highlight clipping

Apple iPhone 14 Pro – wide dynamic range

Honor Magic4 Ultimate – shadow clipping
Color
111
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Image-quality color analysis looks at color rendering, skin-tone rendering, white balance, color shading, stability of the white balance and its adaption when light is changing.
Colors were nice and well-balanced in all indoor and bright light conditions. White balance was generally spot on as well. In low light, some white balance casts were visible. In this clip, a green cast was quite noticeable.
Huawei Mate 50 Pro – slight green cast
Honor Magic4 Ultimate – fairly neutral
Apple iPhone 14 Pro – fairly neutral
Autofocus
111
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Video autofocus was one of the Mate 50 Pro’s major plus points. The system managed to always keep the main subject in focus, and focus transitions were smooth in most cases. This said, our testers observed slightly too abrupt transitions on some occasions as here. But globally, the results were very convincing.
Huawei Mate 50 Pro – accurate focus but slightly too abrupt transitions
Honor Magic4 Ultimate – refocusing
Apple iPhone 14 Pro – smooth focus transitions
Texture
110
Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra
Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra
Texture tests analyze the level of details and texture of the real-life videos as well as the videos of charts recorded in the lab. Natural videos recordings are visually evaluated, with particular attention paid to the level of details in the bright and areas as well as in the dark. Objective measurements are performed of images of charts taken in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux. The charts used are the SBMARK chart (DMC) and Dead Leaves chart.
SBMARK CHART (DMC) detail preservation video score vs lux levels
This graph shows the evolution of the DMC detail preservation video score with the level of lux in video. DMC detail preservation score is derived from an AI-based metric trained to evaluate texture and details rendering on a selection of crops of our SBMARK chart.
Mate 50 Pro video clips generally showed a high level of detail under most conditions. However, some texture artifacts could be quite intrusive, especially under low light. This had a significant impact on the video texture score.
Noise
107
Samsung Galaxy A23 5G
Samsung Galaxy A23 5G
Noise tests analyze various attributes of noise such as intensity, chromaticity, grain, structure, temporal aspects on real-life video recording as well as videos of charts taken in the lab. Natural videos are visually evaluated, with particular attention paid to the noise in the dark areas and high dynamic range conditions. Objective measurements are performed on the videos of charts recorded in various conditions from 1 to 1000 lux. The chart used is the SBMARK visual noise chart.
Spatial visual noise evolution with the illuminance level
This graph shows the evolution of spatial visual noise with the level of lux. Spatial visual noise is measured on the visual noise chart in the video noise setup. SBMARK visual noise measurement is derived from ISO15739 standard.
Temporal visual noise evolution with the illuminance level
This graph shows the evolution of temporal visual noise with the level of lux. Temporal visual noise is measured on the visual noise chart in the video noise setup.
Video noise levels were higher on the Mate 50 Pro than on its direct competitors across pretty much all light conditions.
Stabilization
103
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Apple iPhone 14 Pro Max
Stabilization evaluation tests the ability of the device to stabilize footage thanks to software or hardware technologies such as OIS, EIS, or any others means. The evaluation looks at residual motion, smoothness, jello artifacts and residual motion blur on walk and run use cases in various lighting conditions. The video below is an extract from one of the tested scenes.
Inconsistent sharpness when moving the device while recording video was arguably one of the Mate 50 Pro’s most important drawbacks. The effect was most noticeable when walking while recording. Fairly long exposure times meant that motion blur occurred with every step of the videographer. The images recorded in such a way were stable, but vibrations from the steps were noticeable in the footage.
Huawei Mate 50 Pro – sharpness differences between frames
Honor Magic4 Ultimate – slight sharpness differences between frames
Apple iPhone 14 Pro – no sharpness differences
Artifacts
79
Xiaomi 12S Ultra
Xiaomi 12S Ultra
Artifacts are evaluated with MTF and ringing measurements on the SFR chart in the lab as well as frame-rate measurements using the LED Universal Timer. Natural videos are visually evaluated by paying particular attention to artifacts such as aliasing, quantization, blocking, and hue shift, among others. The more severe and the more frequent the artifact, the higher the point deduction from the score. The main artifacts and corresponding point loss are listed below.
Main video artifacts penalties
Overall, the Mate 50 Pro controlled the most common video artifacts quite well, but some artifacts, including aliasing and ghosting, were still noticeable. Points were also deducted for the 30fps frame rate. Compared to other devices that offer 60fps, the Huawei Mate 50 Pro’s videos were less smooth. This was particularly noticeable when panning.







Start a new Thread